Inter-species cortical registration between macaques and humans using a functional network property under a spherical demons framework
- PMID: 34673832
- PMCID: PMC8530290
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258992
Inter-species cortical registration between macaques and humans using a functional network property under a spherical demons framework
Abstract
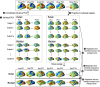
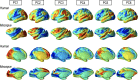
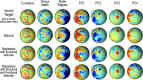
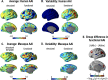
Systematic evaluation of cortical differences between humans and macaques calls for inter-species registration of the cortex that matches homologous regions across species. For establishing homology across brains, structural landmarks and biological features have been used without paying sufficient attention to functional homology. The present study aimed to determine functional homology between the human and macaque cortices, defined in terms of functional network properties, by proposing an iterative functional network-based registration scheme using surface-based spherical demons. The functional connectivity matrix of resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) among cortical parcellations was iteratively calculated for humans and macaques. From the functional connectivity matrix, the functional network properties such as principal network components were derived to estimate a deformation field between the human and macaque cortices. The iterative registration procedure updates the parcellation map of macaques, corresponding to the human connectome project's multimodal parcellation atlas, which was used to derive the macaque's functional connectivity matrix. To test the plausibility of the functional network-based registration, we compared cortical registration using structural versus functional features in terms of cortical regional areal change. We also evaluated the interhemispheric asymmetry of regional area and its inter-subject variability in humans and macaques as an indirect validation of the proposed method. Higher inter-subject variability and interhemispheric asymmetry were found in functional homology than in structural homology, and the assessed asymmetry and variations were higher in humans than in macaques. The results emphasize the significance of functional network-based cortical registration across individuals within a species and across species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

