Early (< 7 days) systemic postnatal corticosteroids for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
- PMID: 34674229
- PMCID: PMC8530019
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001146.pub6
Early (< 7 days) systemic postnatal corticosteroids for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
Abstract
Background: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) remains a major problem for infants born extremely preterm. Persistent inflammation in the lungs is important in its pathogenesis. Systemic corticosteroids have been used to prevent or treat BPD because of their potent anti-inflammatory effects.
Objectives: To examine the relative benefits and adverse effects of systemic postnatal corticosteroids commenced within the first six days after birth for preterm infants at risk of developing BPD.
Search methods: We ran an updated search of the following databases on 25 September 2020: CENTRAL via CRS Web and MEDLINE via OVID. We also searched clinical trials databases and reference lists of retrieved articles for randomised controlled trials (RCTs). We did not include cluster randomised trials, cross-over trials, or quasi-RCTs.
Selection criteria: For this review, we selected RCTs examining systemic (intravenous or oral) postnatal corticosteroid treatment started within the first six days after birth (early) in high-risk preterm infants. We included studies that evaluated the use of dexamethasone, as well as studies that assessed hydrocortisone, even when the latter was used primarily for management of hypotension, rather than for treatment of lung problems. We did not include trials of inhaled corticosteroids.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard Cochrane methods. We extracted and analysed data regarding clinical outcomes that included mortality, BPD, mortality or BPD, failure to extubate, complications during the primary hospitalisation, and long-term health and neurodevelopmental outcomes. We used the GRADE approach to assess the certainty of evidence.
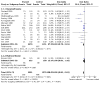
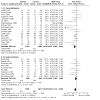
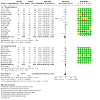
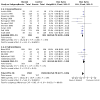
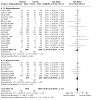
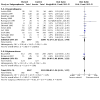
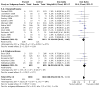
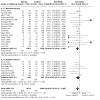
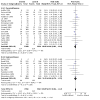
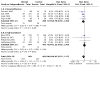
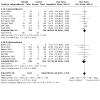
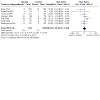
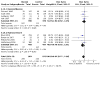
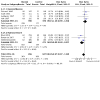
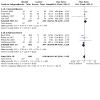
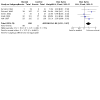
Main results: Use of the GRADE approach revealed that the certainty of evidence was high for the major outcomes considered, except for BPD at 36 weeks for all studies combined, which was downgraded one level to moderate because of evidence of publication bias. We included 32 RCTs (4395 infants). The overall risk of bias of included studies was low; all were RCTs, and most trials used rigorous methods. Early systemic corticosteroids overall have little or no effect on mortality to the latest reported age (risk ratio (RR) 0.95, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.85 to 1.06; 31 studies, 4373 infants; high-certainty evidence), but hydrocortisone alone reduces mortality (RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.65 to 0.99; 11 studies, 1433 infants; high-certainty evidence). Early systemic corticosteroids overall probably reduce BPD at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age (PMA) (RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.73 to 0.88; 26 studies, 4167 infants; moderate-certainty evidence), as does dexamethasone (RR 0.72, 95% CI 0.63 to 0.82; 17 studies, 2791 infants; high-certainty evidence), but hydrocortisone has little to no effect (RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.06; 9 studies, 1376 infants; high-certainty evidence). Early systemic corticosteroids overall reduce the combined outcome of mortality or BPD at 36 weeks' PMA (RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.84 to 0.94; 26 studies, 4167 infants; high-certainty evidence), as do both dexamethasone (RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.81 to 0.95; 17 studies, 2791 infants; high-certainty evidence) and hydrocortisone (RR 0.90, 95% CI 0.82 to 0.99; 9 studies, 1376 infants; high-certainty evidence). Early systemic corticosteroids overall increase gastrointestinal perforation (RR 1.84, 95% CI 1.36 to 2.49; 16 studies, 3040 infants; high-certainty evidence), as do both dexamethasone (RR 1.73, 95% CI 1.20 to 2.51; 9 studies, 1936 infants; high-certainty evidence) and hydrocortisone (RR 2.05, 95% CI 1.21 to 3.47; 7 studies, 1104 infants; high-certainty evidence). Early systemic corticosteroids overall increase cerebral palsy (RR 1.43, 95% CI 1.07 to 1.92; 13 studies, 1973 infants; high-certainty evidence), as does dexamethasone (RR 1.77, 95% CI 1.21 to 2.58; 7 studies, 921 infants; high-certainty evidence) but not hydrocortisone (RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.66 to 1.66; 6 studies, 1052 infants; high-certainty evidence). Early systemic corticosteroids overall have little to no effect on the combined outcome of mortality or cerebral palsy (RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.16; 13 studies, 1973 infants; high-certainty evidence), nor does hydrocortisone (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.71 to 1.05; 6 studies, 1052 infants; high-certainty evidence). However, early dexamethasone probably increases the combined outcome of mortality or cerebral palsy (RR 1.18, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.37; 7 studies, 921 infants; high-certainty evidence), In sensitivity analyses by primary intention for treatment with hydrocortisone (lung problems versus hypotension), there was little evidence of differences in effects on major outcomes of mortality, BPD, or combined mortality or BPD, by indication for the drug.
Authors' conclusions: Early systemic postnatal corticosteroid treatment (started during the first six days after birth) prevents BPD and the combined outcome of mortality or BPD. However, it increases risks of gastrointestinal perforation, cerebral palsy, and the combined outcome of mortality or cerebral palsy. Most beneficial and harmful effects are related to early treatment with dexamethasone, rather than to early treatment with hydrocortisone, but early hydrocortisone may prevent mortality, whereas early dexamethasone does not. Longer-term follow-up into late childhood is vital for assessment of important outcomes that cannot be assessed in early childhood, such as effects of early corticosteroid treatment on higher-order neurological functions, including cognitive function, executive function, academic performance, behaviour, mental health, motor function, and lung function. Further RCTs of early corticosteroids, particularly of hydrocortisone, should include longer-term survival free of neurodevelopmental disability as the primary outcome.
Copyright © 2021 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Jeanie Cheong received a Career Development Fellowship, for salary support, from the Australian Medical Research Future Fund.
Lex Doyle's institution received grant funding from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) of Australia.
Henry Halliday declared no conflicts of interest.
Susanne Hay was the PI on a network meta‐analysis of systemic corticosteroids for bronchopulmonary dysplasia, for which her institution received a grant from the Deborah Munroe Noonan Memorial Research Fund. She works as a neonatologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Brett Manley's institution received funding for a Career Development Fellowship from the Australian Medical Research Future Fund. His institution also received project grant funding from the NHMRC of Australia. He has published articles and review articles on the topic of postnatal steroids in peer‐reviewed journals, and has commented on social media. He works as a Consultant Neonatologist at The Royal Women's Hospital, Parkville, Victoria, Australia.
Figures




































Update of
-
Early (< 8 days) systemic postnatal corticosteroids for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 24;10(10):CD001146. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001146.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 21;10:CD001146. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001146.pub6. PMID: 29063585 Free PMC article. Updated.
Comment in
-
Commentary on "Early (<7 Days) Systemic Postnatal Corticosteroids for Prevention of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Preterm Infants".Neonatology. 2023;120(6):805-811. doi: 10.1159/000532079. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Neonatology. 2023. PMID: 37699378 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Anttila 2005 {published data only}
-
- Anttila E, Peltonemi O, Haumont D, Herting E, ter Horst H, Heinonen K, et al.Early neonatal dexamethasone treatment for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Randomised trial and meta-analysis evaluating the duration of dexamethasone therapy. European Journal of Pediatrics 2005;164(8):472-81. [DOI: 10.1007/s00431-005-1645-8] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Baden 1972 {published data only}
-
- Baden M, Bauer CR, Cole E, Klein G, Taeusch HW, Stern L.A controlled trial of hydrocortisone therapy in infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics 1972;50(4):526-34. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Fitzhardinge PM, Eisen A, Lejtenyi C, Metrakos K, Ramsay M.Sequelae of early steroid administration to the newborn infant. Pediatrics 1974;53(6):877-83. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Batton 2012 {published data only}
-
- Batton BJ, Li L, Newman NS, Das A, Watterberg KL, Yoder BA, et al, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network.Feasibility study of early blood pressure management in extremely preterm infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2012;161(1):65-9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.01.014] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Baud 2016 {published data only}
-
- Baud O, Biran V, Trousson C, Leroy E, Mohamed D, Alberti C.Two-year outcomes after prophylactic hydrocortisone in extremely preterm neonates. In: European Journal of Pediatrics. Vol. 175. 2016:1507.
-
- Baud O, Maury L, Lebail F, Ramful D, El Moussawi F, Nicaise C, et al, PREMILOC Trial Study Group.Effect of early low-dose hydrocortisone on survival without bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely preterm infants (PREMILOC): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet 2016;387(10030):1827-36. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00202-6] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baud O, Trousson C, Biran V, Leroy E, Mohamed D, Alberti C, PREMILOC Trial Group.Association between early low-dose hydrocortisone therapy in extremely preterm neonates and neurodevelopmental outcomes at 2 years of age. JAMA 2017;317(13):1329-37. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.2692] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Biswas 2003 {published data only}
-
- Biswas S, Buffery J, Enoch H, Bland M, Markiewicz M, Walters D.Pulmonary effects of triiodothyronine (T3) and hydrocortisone (HC) supplementation in preterm infants less than 30 weeks gestation: results of the THORN trial - thyroid hormone replacement in neonates. Pediatric Research 2003;53(1):48-56. [DOI: 10.1203/00006450-200301000-00011] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Biswas S.Personal communication. email 2002.
Bonsante 2007 {published data only}
Efird 2005 {published data only}
Garland 1999 {published data only}
Halac 1990 {published data only}
Hochwald 2014 {published data only}
Kopelman 1999 {published data only}
Lauterbach 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lauterbach R, Szymura-Oleksiak J, Pawlik D, Warchol J, Lisowska-Miszczyk I, Rytlewski K.Nebulized pentoxifylline for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in very low birth weight infants: a pilot clinical study. Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2006;19(7):433-8. [DOI: 10.1080/14767050600736754] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Lin 1999 {published data only}
Mukhopadhyay 1998 {published data only}
-
- Mukhopadhyay K, Kumar P, Narang A.Role of early postnatal dexamethasone in respiratory distress syndrome. Indian Pediatrics 1998;35(2):117-22. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ng 2006 {published data only}
Peltoniemi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Peltoniemi O, Kari A, Heinonen K, Saarela T, Nikolajev K, Andersson S, et al.Pretreatment cortisol values may predict responses to hydrocortisone administration for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in high-risk infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2005;146(5):632-7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.12.040] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Peltoniemi OM, Lano A, Yliherva A, Kari MA, Hallman M, Neonatal Hydrocortisone Working Group.Randomised trial of early neonatal hydrocortisone demonstrates potential undesired effects on neurodevelopment at preschool age. Acta Paediatrica 2016;105(2):159-64. [DOI: 10.1111/apa.13074] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Rastogi 1996 {published data only}
-
- Rastogi A, Akintorin SM, Bez ML, Morales P, Pildes PS.A controlled trial of dexamethasone to prevent bronchopulmonary dysplasia in surfactant-treated infants. Pediatrics 1996;98(2 Pt 1):204-10. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Romagnoli 1999 {published data only}
-
- Romagnoli C, Zecca E, Luciano R, Torrioli G, Tortorolo G.Controlled trial of early dexamethasone treatment for the prevention of chronic lung disease in preterm infants: a 3-year follow-up. Pediatrics 2002;109(6):e85. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sanders 1994 {published data only}
-
- Sanders RJ, Cox C, Phelps DL, Sinkin RA.Two doses of early intravenous dexamethasone for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in babies with respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatric Research 1994;36(1 Pt 1):122-8. [DOI: 10.1203/00006450-199407001-00022] [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Sinkin RA.Personal communication. email 2002.
Shinwell 1996 {published data only}
-
- Shinwell ES, Karplus M, Zmora E, Reich D, Rothschild A, Blazer S, et al.Failure of early postnatal dexamethasone to prevent chronic lung disease in infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Edition 1996;74(1):F33-7. [DOI: 10.1136/fn.74.1.f33] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shinwell ES.Early dexamethasone therapy is associated with increased incidence of cerebral palsy. Hot Topics' 99 in Neonatology 1999:240-54.
-
- Shinwell ES.Personal communication. email 2002.
Sinkin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Sinkin RA.Personal communication. email 2002.
Soll 1999 {published data only}
-
- Soll RF, Vermont Oxford Network Steroid Study Group.Early postnatal dexamethasone therapy for the prevention of chronic lung disease. Pediatric Research 1999;45:226A. - PubMed
Stark 2001 {published data only}
-
- Stark AR, Carlo WA, Tyson JE, Papile LA, Wright LL, Shankaran S, et al, National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network.Adverse effects of early dexamethasone in extremely-low-birth-weight infants. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;344(2):95-101. [DOI: 10.1056/NEJM200101113440203] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stark AR, Carlo WA, Vohr BR, Papile L, Saha S, Bauer CR, et al, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network.Death or neurodevelopmental impairment at 18 to 22 months corrected age in a randomized trial of early dexamethasone to prevent death or chronic lung disease in extremely low birth weight infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2014;164(1):34-9 e2. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.07.027] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Subhedar 1997 {published data only}
-
- Subhedar NV.Personal communication. email 2002.
Suske 1996 {published data only}
Tapia 1998 {published data only}
-
- Tapia JL, Ramirez R, Cifuentes J, Fabres J, Hubner ME, Bancalari A, et al.The effect of early dexamethasone administration on bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Journal of Pediatrics 1998;132(1):48-52. [DOI: 10.1016/s0022-3476(98)70483-4] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Vento 2004 {published data only}
Wang 1996 {published data only}
-
- Wang JY, Yeh TF, Lin YJ, Chen WY, Lin CH.Early postnatal dexamethasone therapy may lessen lung inflammation in premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome on mechanical ventilation. Pediatric Pulmonology 1997;23(3):193-7. [DOI: 10.1002/(sici)1099-0496(199703)23:3<193::aid-ppul4>3.0.co;2-p] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Watterberg 1999 {published data only}
Watterberg 2004 {published data only}
Yeh 1990 {published data only}
Yeh 1997 {published data only}
-
- Yeh TF, Lin I, Shieh W, Lin H, Chen J, Kao S.Prevention of chronic lung disease (CLD) in premature RDS infants with early and prolonged dexamethasone (D) therapy - a multicenter double-blind controlled study. Pediatric Research 1994;35(4):262A.
-
- Yeh TF, Lin YJ, Hsieh WS, Lin HC, Lin CH, Chen JY, et al.Early postnatal dexamethasone therapy for the prevention of chronic lung disease in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome: a multicenter clinical trial. Pediatrics 1997;100(4):E3. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.100.4.e3] [PMID: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ariagno 1987 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ariagno RL, Sweeney TE, Baldwin RB, Inguillo D, Martin D.Controlled trial of dexamethasone in preterm infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia: lung function, clinical course and outcome at three years (as supplied 2000). Data on file.
-
- Ariagno RL, Sweeney TJ, Baldwin RB, Inguillo D, Martin D.Dexamethasone effects on lung function and risks in 3 week old ventilatory dependent preterm infants. American Reviews of Respiratory Disease 1987;135:A125.
Avery 1985 {published data only}
-
- Avery GB, Fletcher AB, Kaplan M, Brudno DS.Controlled trial of dexamethasone in respirator-dependent infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics 1985;75(1):106-11. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bouchier 1997 {published data only}
Brozanski 1995 {published data only}
-
- Brozanski BS, Jones JG, Gilmour CH, Balsan MJ, Vazquez RL, Israel BA, et al.Effect of pulse dexamethasone therapy on the incidence and severity of chronic lung disease in the very low birth weight infant. Journal of Pediatrics 1995;126(5 Pt 1):769-76. [DOI: 10.1016/s0022-3476(95)70410-8] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gilmour CH, Sentipal-Walerius JM, Jones JG, Doyle JM, Brozanski BS, Balsan MJ, et al.Pulse dexamethasone does not impair growth and body composition of very low birth weight infants. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 1995;14(5):455-62. [DOI: 10.1080/07315724.1995.10718536] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hofkosh D, Brozanski BS, Edwards DE, Williams LA, Jones JG, Cheng KP.One year outcome of infants treated with pulse dexamethasone for prevention of BPD. Pediatric Research 1995;37(4):259A.
CDTG 1991 {published data only}
-
- Collaborative Dexamethasone Trial Group.Dexamethasone therapy in neonatal chronic lung disease: an international placebo-controlled trial. Pediatrics 1991;88(3):421-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Jones R, Wincott E, Elbourne D, Grant A.Controlled trial of dexamethasone in neonatal chronic lung disease: a 3-year follow-up. Pediatrics 1995;96(5 Pt 1):897-906. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Jones RA, Collaborative Dexamethasone Trial Follow-up Group.Randomized, controlled trial of dexamethasone in neonatal chronic lung disease: 13- to 17-year follow-up study: I. Neurologic, psychological, and educational outcomes. Pediatrics 1995;116(2):370-8. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2004-1818] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jones RA, Collaborative Dexamethasone Trial Follow-up Group.Randomized, controlled trial of dexamethasone in neonatal chronic lung disease: 13- to 17-year follow-up study: II. Respiratory status, growth, and blood pressure. Pediatrics 2005;116(2):379-84. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2004-1819] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Cummings 1989 {published data only}
-
- Cummings JJ.Personal communication. email 2002.
Dobryansky 2012 {published data only}
-
- Dobryansky D, Borysiuk O, Salabay Z, Dubrovna Y.Clinical effectiveness of early administration of caffeine and low-dose hydrocortisone to preterm newborns with a high risk of BPD development. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2012;97:A119. [DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2012-302724.0405] - DOI
Doyle 2006 {published data only}
-
- Doyle LW, Davis PG, Morley CJ, McPhee A, Carlin JB, DART Study Investigators.Outcome at 2 years of age of infants from the DART study: a multicenter, international, randomized, controlled trial of low-dose dexamethasone. Pediatrics 2007;119(4):716-21. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2006-2806] [PMID: 17403842 ] - DOI - PubMed
Durand 1995 {published data only}
-
- Durand M, Sardesai S, McEvoy C.Effects of early dexamethasone therapy on pulmonary mechanics and chronic lung disease in very low birth weight infants: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 1995;95(4):584-90. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Gaissmaier 1999 {published data only}
Gross 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gross SJ, Anbar RD, Mettelman BB.Follow-up at 15 years of preterm infants from a controlled trial of moderately early dexamethasone for the prevention of chronic lung disease. Pediatrics 2005;115(3):681-7. [10.1542/peds.2004-0956] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Harkavy 1989 {published data only}
Kari 1993 {published data only}
-
- Mieskonen S, Eronen M, Malmberg LP, Turpeinen M, Kari MA, Hallman M.Controlled trial of dexamethasone in neonatal chronic lung disease: an 8-year follow-up of cardiopulmonary function and growth. Acta Paediatrica 2003;92(8):896-904. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kazzi 1990 {published data only}
-
- Kazzi NJ, Brans YW, Poland RL.Dexamethasone effects on the hospital course of infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia who are dependent on artificial ventilation. Pediatrics 1990;86(5):722-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Kothadia 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bensky AS, Kothadia JM, Covitz W.Cardiac effects of dexamethasone in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 1996;97(6 Pt 1):818-21. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Goldstein DJ, Waldrep EL, VanPelt JC, O'Shea TM.Developmental outcome at 5 years following dexamethasone use for very low birth weight infants. Pediatric Research 2000;47(4):310A.
-
- Kothadia JM, O'Shea TM, Roberts D, Auringer ST, Weaver RG 3rd, Dillard RG.Randomized placebo-controlled trial of a 42-day tapering course of dexamethasone to reduce the duration of ventilator dependency in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 1999;104(1 Pt 1):22-7 Erratum in: Pediatrics 2004;114(6):1746. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.104.1.22] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nixon PA, Washburn LK, Schechter MS, O'Shea TM.Follow-up study of a randomized controlled trial of postnatal dexamethasone therapy in very low birth weight infants: effects on pulmonary outcomes at age 8 to 11 years. Journal of Pediatrics 2007;150(4):345-50. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2006.12.013] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- O'Shea TM, Goldstein DJ, Jackson BG, Kothadia JM, Dillard RG.Randomized trial of a 42-day tapering course of dexamethasone in very low birth weight infants: neurological, medical and functional outcome at 5 years of age. Pediatric Research 2000;47(4):319A. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.04.047] [PMID: 31349916] - DOI - PubMed
Kovacs 1998 {published data only}
Noble‐Jamieson 1989 {published data only}
Ohlsson 1992 {published data only}
-
- Ohlsson A, Calvert SA, Hosking M, Shennan AT.Randomized controlled trial of dexamethasone treatment in very-low-birth-weight infants with ventilator-dependent chronic lung disease. Acta Paediatrica 1992;81(10):751-6. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1992.tb12096.x] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Onland 2019 {published data only}
-
- Onland W, Cools F, Kroon A, Rademaker K, Merkus MP, Dijk PH, et al, Stop-BPD Study Group.Effect of hydrocortisone therapy initiated 7 to 14 days after birth on mortality or bronchopulmonary dysplasia among very preterm infants receiving mechanical ventilation: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2019;321:354-63. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.21443] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Papile 1998 {published data only}
Parikh 2013 {published data only}
Romagnoli 1997 {published data only}
-
- Romagnoli C, Vento G, Zecca E, Tortorolo G, Papacci P, De Carolis M, et al.Dexamethasone for the prevention of chronic lung disease in preterm neonates: a prospective randomized study [II desametazone nella prevenzione della patologia polmonare cronica del neonato pretermine: studio prospettico randomizzato]. Rivista Italiana di Pediatria [Italian Journal of Pediatrics] 1997;24:283-8.
Salas 2014 {published data only}
-
- Salas G, Travaglianti M, Leone A, Couceiro C, Rodríguez S, Fariña D.Hydrocortisone for the treatment of refractory hypotension:a randomised controlled trial [Hidrocortisona para el tratamiento de hipotensión refractaria: ensayo clínico controlado y aleatorizado]. Anales de Pediatria 2014;80(6):387-93. [DOI: 10.1016/j.anpedi.2013.08.004] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Scott 1997 {published data only}
-
- Scott SM, Backstrom C, Bessman S.Effect of five days of dexamethasone therapy on ventilator dependence and adrenocorticotropic hormone-stimulated cortisol concentrations. Journal of Perinatology 1997;17(1):24-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Smolkin 2014 {published data only}
-
- Smolkin T, Ulanovsky I, Jubran H, Blazer S, Makhoul IR.Experience with oral betamethasone in extremely low birthweight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Edition 2014;99(6):F517-8. [DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2014-306619] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Tsukahara 1999 {published data only}
Vincer 1998 {published data only}
-
- Vincer MJ, Allen AC.Double blind randomized controlled trial of 6-day pulse of dexamethasone for very low birth weight infants (VLBW <1500 grams) who are ventilator dependent at 4 weeks of age. Pediatric Research 1998;43:201A.
Walther 2003 {published data only}
Yaseen 1999 {published data only}
Yates 2019 {published data only}
-
- Yates H, Chiocchia V, Linsell L, Orsi N, Juszczak E, Johnson K, et al.Very low-dose dexamethasone to facilitate extubation of preterm babies at risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: the MINIDEX feasibility RCT. Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation 2019;6:8. [DOI: 10.3310/eme06080] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Additional references
Anonymous 1991
-
- [No authors listed].Dexamethasone for neonatal chronic lung disease. Lancet 1991;338(8773):982-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Arias‐Camison 1999
-
- Arias-Camison JM, Lau J, Cole CH, Frantz ID 3rd.Meta-analysis of dexamethasone therapy started in the first 15 days of life for prevention of chronic lung disease in premature infants. Pediatric Pulmonology 1999;28(3):167-74. [DOI: 10.1002/(sici)1099-0496(199909)28:3<167::aid-ppul2>3.0.co;2-y] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Baud 1999
Bayley 1993
-
- Bayley, N.Bayley Scales of Infant Development. 2nd edition. San Antonio: The Psychological Corporation, 1993.
Bhuta 1998
Cheong 2020
-
- Cheong JL, Olsen JE, Huang L, Dalziel KM, Boland RA, Burnett AC, et al, Members of the Victorian Infant Collaborative Study Group.Changing consumption of resources for respiratory support and short-term outcomes in four consecutive geographical cohorts of infants born extremely preterm over 25 years since the early 1990s. BMJ Open 2020;10(9):e037507. [DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037507] [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Doyle 2000
Doyle 2010a
Doyle 2010b
Doyle 2010c
Doyle 2014b
Doyle 2017b
Egberts 1997
-
- Egberts J, Brand R, Walti H, Bevilacqua G, Breart G, Gardini F.Mortality, severe respiratory distress syndrome and chronic lung disease of the newborn are reduced more after prophylactic than after therapeutic administration of the surfactant Curosurf. Pediatrics 1997;100(1):E4. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.100.1.e4] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Fitzhardinge 1974
-
- Fitzhardinge PM, Eisen A, Lejtenyi C, Metrakos K, Ramsay M.Sequelae of early steroid administration to the newborn infant. Pediatrics 1974;53(6):877-83. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Gibson 1993
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- GRADE Working Group, McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime) GRADEpro GDT.Version accessed 21 February 2017. Hamilton (ON): GRADE Working Group, McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime).
Gramsbergen 1998
Groneck 1995
Halliday 1997
-
- Halliday HL.A review of postnatal corticosteroids for treatment and prevention of chronic lung disease in the preterm infant. Prenatal and Neonatal Medicine 1997;2:1-12.
Halliday 1999
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Sterne JA, on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group and the Cochrane Bias Methods Group.Chapter 8. Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2020
-
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al (editors).Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). Cochrane, 2020. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Mammel 1983
Ng 1993
Onland 2017
Ovelman 2020
-
- Ovelman C, Eckert C, Friesen C.Validating Cochrane Neonatal’s standard search databases: is it okay to stop searching Embase? In: Advances in Evidence Synthesis: special issue. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD202001/full. 2020; (9 Suppl 1): [320].
Papile 1996
-
- Papile LA, Stoll B, Donovan E, Tyson I, Bauer C, Wright L, et al.Dexamethasone therapy in infants at risk for chronic lung disease (CLD): a multicenter, randomized, double-masked trial. Pediatric Research 1996;39:236A. [DOI: 10.1203/00006450-199604001-01422] - DOI
Peltoniemi 2009
Peltoniemi 2016
-
- Peltoniemi OM, Lano A, Yliherva A, Kari MA, Hallman M, Neonatal Hydrocortisone Working Group.Randomised trial of early neonatal hydrocortisone demonstrates potential undesired effects on neurodevelopment at preschool age. Acta Paediatrica 2016;105(2):159-64. [DOI: 10.1111/apa.13074] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Review Manager 2020 [Computer program]
-
- The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5).Version 5.4. Copenhagen: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020.
Romagnoli 2002
Ryan 1996
Schmidt 2006
Schünemann 2013
-
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editor(s).Handbook for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations using the GRADE approach (updated October 2013). GRADE Working Group, 2013. Available from gdt.guidelinedevelopment.org/app/handbook/handbook.html.
Shaffer 2019
-
- Shaffer MI, Baud O, Lacaze-Masmonteil T, Peltoniemi OM, Bonsante F, Watterberg KL.Effect of prophylaxis for early adrenal insufficiency using low-dose hydrocortisone in very preterm infants: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Journal of Pediatrics 2019;207:136-42. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.10.004] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Shah 2007b
-
- Shah V, Ohlsson A, Halliday H, Dunn MS.Early administration of inhaled corticosteroids for preventing chronic lung disease in ventilated very low birth weight preterm neonates. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007, Issue 4. Art. No: CD001969. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001969.pub2] - DOI - PubMed
Shah 2012a
Shah 2012b
-
- Shah SS, Ohlsson A, Halliday HL, Shah VS.Inhaled versus systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic lung disease in ventilated very low birth weight preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 5. Art. No: CD002057. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002057.pub3] - DOI - PubMed
Shah 2017
-
- Shahh VS, Ohlsson A, Halliday HL, Dunn M.Early administration of inhaled corticosteroids for preventing chronic lung disease in very low birth weight preterm neonates. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017, Issue 1. Art. No: CD001969. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001969.pub4] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Shinwell 2002
Stanley 1982
Stark 2014
-
- Stark AR, Carlo WA, Vohr BR, Papile LA, Saha S, Bauer CR, et al, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network.Death or neurodevelopmental impairment at 18 to 22 months corrected age in a randomized trial of early dexamethasone to prevent death or chronic lung disease in extremely low birth weight infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2014;164(1):34-9 e2. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.07.027] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Tarnow‐Mordi 1999
Tschanz 1995
van Goudoever 1994
Watterberg 2007
Weichsel 1977
Werner 1992
Yeh 1998
-
- Yeh TF, Lin YJ, Huang CC, Chen YJ, Lin CH, Lin HC, et al.Early dexamethasone therapy in preterm infants: a follow up study. Pediatrics 1998;101(5):E7. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.101.5.e7] [PMID: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Doyle 2014a
Doyle 2017a
Halliday 2000
Halliday 2001
Halliday 2003
Halliday 2009
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

