Induced pluripotent stem cells can improve thrombolytic effect of low-dose rt-PA after acute carotid thrombosis in rat
- PMID: 34674761
- PMCID: PMC8532293
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-021-02615-z
Induced pluripotent stem cells can improve thrombolytic effect of low-dose rt-PA after acute carotid thrombosis in rat
Abstract
Background: Intravenous thrombolysis using recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) is the standard treatment for acute ischemic stroke. Standard-dose rt-PA (0.9 mg/kg) is known to achieve good recanalization but carries a high bleeding risk. Lower dose of rt-PA has less bleeding risk but carries a high re-occlusion rate. We investigate if induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) can improve the thrombolytic effect of low-dose rt-PA (0.45 mg/kg).
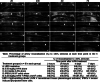
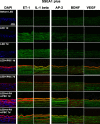
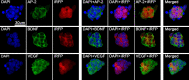
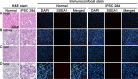
Methods: Single irradiation with 6 mW/cm2 light-emitting diode (LED) for 4 h at rat common carotid artery was used as thrombosis model according to our previous report. Endothelin-1 (ET-1), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and interleukin 1 beta (IL-1 beta) were used as the inflammatory markers for artery endothelial injury. Angiopoietin-2 (AP-2), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were examined in artery wall and iPSCs culture. Animal ultrasound was used to evaluate the stenosis degree of common carotid artery before and at 2 h, 24 h, 4 days and 7 days after LED irradiation.
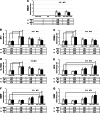
Results: After LED irradiation alone, there was a persistent occlusion from 2 h to 7 days. Standard-dose rt-PA alone could recanalize the occluded artery from 24 h to 7 days to stenotic degree ≤ 50%. Low-dose rt-PA or 1 × 106 mouse iPSCs alone could not recanalize the occluded arteries from 2 h to 7 days. Combination use of low-dose rt-PA plus 1 × 106 mouse iPSCs caused better recanalization from 24 h to 7 days. ET-1, ICAM-1 and IL-1 beta were strongly expressed after LED irradiation but reduced after iPSCs treatment. AP-2, BDNF and VEGF were rarely induced after LED irradiation but strongly expressed after iPSCs treatment. In vitro study showed iPSCs could express AP-2, BDNF and VEGF.
Conclusion: The adjuvant use of iPSCs may help improving the thrombolytic effect of low-dose rt-PA by suppressing inflammatory factors and inducing angiogenic trophic factors. Stem cells could be a potential regimen in acute thrombolytic therapy to improve recanalization and reduce complications.
Keywords: Carotid thrombosis; Endothelium; Stem cell; Thrombolysis; Tissue plasminogen activator.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Function of tissue-type plasminogen activator releaser on vascular endothelial cells and thrombolysis in vivo.Thromb Haemost. 2002 Jun;87(6):1069-74. Thromb Haemost. 2002. PMID: 12083488
-
Tirofiban combined with rt-PA intraarterial thrombolysis improves the recanalization rate of acute middle cerebral artery occlusion in rabbits.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 May;22(9):2888-2895. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201805_14991. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29771445
-
Recanalization therapies for acute ischemic stroke.Semin Neurol. 1998;18(4):471-84. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040900. Semin Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9932618 Review.
-
Response to intra-arterial and combined intravenous and intra-arterial thrombolytic therapy in patients with distal internal carotid artery occlusion.Stroke. 2002 Jul;33(7):1821-6. doi: 10.1161/01.str.0000020363.23725.67. Stroke. 2002. PMID: 12105360
-
Therapeutic ultrasound in ischemic stroke treatment: experimental evidence.Eur J Ultrasound. 2002 Nov;16(1-2):121-30. doi: 10.1016/s0929-8266(02)00049-6. Eur J Ultrasound. 2002. PMID: 12470857 Review.
Cited by
-
Stem cell-based ischemic stroke therapy: Novel modifications and clinical challenges.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2024 Feb;19(1):100867. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100867. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38357525 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feigin VL, Roth GA, Naghavi M, Parmar P, Krishnamurthi R, Chugh S, et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(9):913–924. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30073-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- National Institute of Neurological D, Stroke rt PASSG. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(24):1581–7. 10.1056/NEJM199512143332401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

