Neural stem/precursor cells dynamically change their epigenetic landscape to differentially respond to BMP signaling for fate switching during brain development
- PMID: 34675062
- PMCID: PMC8559679
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.348797.121
Neural stem/precursor cells dynamically change their epigenetic landscape to differentially respond to BMP signaling for fate switching during brain development
Abstract
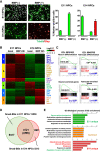
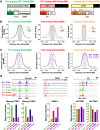
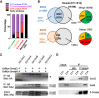
During neocortical development, tight regulation of neurogenesis-to-astrogenesis switching of neural precursor cells (NPCs) is critical to generate a balanced number of each neural cell type for proper brain functions. Accumulating evidence indicates that a complex array of epigenetic modifications and the availability of extracellular factors control the timing of neuronal and astrocytic differentiation. However, our understanding of NPC fate regulation is still far from complete. Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are renowned as cytokines that induce astrogenesis of gliogenic late-gestational NPCs. They also promote neurogenesis of mid-gestational NPCs, although the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. By performing multiple genome-wide analyses, we demonstrate that Smads, transcription factors that act downstream from BMP signaling, target dramatically different genomic regions in neurogenic and gliogenic NPCs. We found that histone H3K27 trimethylation and DNA methylation around Smad-binding sites change rapidly as gestation proceeds, strongly associated with the alteration of accessibility of Smads to their target binding sites. Furthermore, we identified two lineage-specific Smad-interacting partners-Sox11 for neurogenic and Sox8 for astrocytic differentiation-that further ensure Smad-regulated fate-specific gene induction. Our findings illuminate an exquisite regulation of NPC property change mediated by the interplay between cell-extrinsic cues and -intrinsic epigenetic programs during cortical development.
Keywords: epigenetic modifications; Smad; astrocyte; bone morphogenetic protein; chromatin accessibility; differentiation; neural stem/precursor cell; neuron.
© 2021 Katada et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SoxE group transcription factor Sox8 promotes astrocytic differentiation of neural stem/precursor cells downstream of Nfia.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021 Dec;9(6):e00749. doi: 10.1002/prp2.749. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021. PMID: 34677001 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging mechanisms underlying astrogenesis in the developing mammalian brain.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2017;93(6):386-398. doi: 10.2183/pjab.93.024. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28603210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High mobility group nucleosome-binding family proteins promote astrocyte differentiation of neural precursor cells.Stem Cells. 2014 Nov;32(11):2983-97. doi: 10.1002/stem.1787. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 25069414
-
BMP/SMAD Pathway Promotes Neurogenesis of Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons In Vivo and in Human Induced Pluripotent and Neural Stem Cells.J Neurosci. 2018 Feb 14;38(7):1662-1676. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1540-17.2018. Epub 2018 Jan 10. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29321139 Free PMC article.
-
Cell fate determination regulated by a transcriptional signal network in the developing mouse brain.Anat Sci Int. 2005 Mar;80(1):12-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-073x.2005.00097.x. Anat Sci Int. 2005. PMID: 15794126 Review.
Cited by
-
Stuck on you: Meninges cellular crosstalk in development.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2023 Apr;79:102676. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2023.102676. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36773497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of neural stem cell aging in the mouse hippocampus by Setd8 downregulation.EMBO J. 2025 Jul;44(13):3645-3668. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00455-8. Epub 2025 Jun 3. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 40461639 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous neural stem cells characterization using omics approaches: Current knowledge in health and disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Apr 5;17:1125785. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1125785. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37091923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Research of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in the Treatment of Maxillofacial Neurological Disorders and the Promotion of Facial Nerve Regeneration.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr 28. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04981-8. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40295362 Review.
-
Tip60/KAT5 Histone Acetyltransferase Is Required for Maintenance and Neurogenesis of Embryonic Neural Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2113. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032113. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768434 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
