Screening and predicted value of potential biomarkers for breast cancer using bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 34675265
- PMCID: PMC8531389
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-00268-9
Screening and predicted value of potential biomarkers for breast cancer using bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
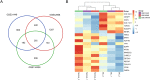
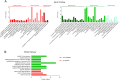
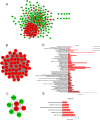
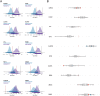
Breast cancer is the most common cancer and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women. Increasing molecular targets have been discovered for breast cancer prognosis and therapy. However, there is still an urgent need to identify new biomarkers. Therefore, we evaluated biomarkers that may aid the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. We searched three mRNA microarray datasets (GSE134359, GSE31448 and GSE42568) and identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) by comparing tumor and non-tumor tissues using GEO2R. Functional and pathway enrichment analyses of the DEGs were performed using the DAVID database. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was plotted with STRING and visualized using Cytoscape. Module analysis of the PPI network was done using MCODE. The associations between the identified genes and overall survival (OS) were analyzed using an online Kaplan-Meier tool. The redundancy analysis was conducted by DepMap. Finally, we verified the screened HUB gene at the protein level. A total of 268 DEGs were identified, which were mostly enriched in cell division, cell proliferation, and signal transduction. The PPI network comprised 236 nodes and 2132 edges. Two significant modules were identified in the PPI network. Elevated expression of the genes Discs large-associated protein 5 (DLGAP5), aurora kinase A (AURKA), ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 C (UBE2C), ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2(RRM2), kinesin family member 23(KIF23), kinesin family member 11(KIF11), non-structural maintenance of chromosome condensin 1 complex subunit G (NCAPG), ZW10 interactor (ZWINT), and denticleless E3 ubiquitin protein ligase homolog(DTL) are associated with poor OS of breast cancer patients. The enriched functions and pathways included cell cycle, oocyte meiosis and the p53 signaling pathway. The DEGs in breast cancer have the potential to become useful targets for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of candidate biomarkers and analysis of prognostic values in ovarian cancer by integrated bioinformatics analysis.Med Oncol. 2016 Nov;33(11):130. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0840-y. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Med Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27757782
-
Identification of candidate biomarkers and pathways associated with SCLC by bioinformatics analysis.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Aug;18(2):1538-1550. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9095. Epub 2018 May 29. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29845250 Free PMC article.
-
Screening Hub Genes as Prognostic Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Bioinformatics Analysis.Cell Transplant. 2019 Dec;28(1_suppl):76S-86S. doi: 10.1177/0963689719893950. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Cell Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31822116 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of breast cancer hub genes and analysis of prognostic values using integrated bioinformatics analysis.Cancer Biomark. 2017 Dec 12;21(1):373-381. doi: 10.3233/CBM-170550. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 29081411
-
Demystifying the Role of Prognostic Biomarkers in Breast Cancer through Integrated Transcriptome and Pathway Enrichment Analyses.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Mar 16;13(6):1142. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13061142. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980449 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
DLGAP5 Regulates the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Cell Cycle of Breast Cancer Cells via the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31;24(21):15819. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115819. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958803 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for Breast Adenocarcinoma Using In Silico Approaches.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Mar 3;2022:7825272. doi: 10.1155/2022/7825272. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Aug 9;2023:9812108. doi: 10.1155/2023/9812108. PMID: 35280505 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Validation of a Disease-Free Survival Prediction Model Using UBE2C and Clinical Indicators in Breast Cancer Patients.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2023 Apr 25;15:295-310. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S402109. eCollection 2023. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2023. PMID: 37139241 Free PMC article.
-
Computational molecular insights into ibrutinib as a potent inhibitor of HER2-L755S mutant in breast cancer: gene expression studies, virtual screening, docking, and molecular dynamics analysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Mar 19;12:1510896. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1510896. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40177517 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of DLGAP5 by AR suppresses p53 signaling and inhibits CD8+T cell infiltration in triple-negative breast cancer.Transl Oncol. 2024 Nov;49:102081. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102081. Epub 2024 Aug 24. Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39182361 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

