Vitamin D status in very low birth weight infants and response to vitamin D intake during their NICU stays: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 34675370
- PMCID: PMC8528940
- DOI: 10.1038/s41372-021-01238-9
Vitamin D status in very low birth weight infants and response to vitamin D intake during their NICU stays: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate vitamin D status in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants and response to vitamin D intake.
Study design: In this prospective cohort study of VLBW infants, 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] was measured regularly starting at birth. Daily vitamin D intake was estimated from parenteral and enteral sources.
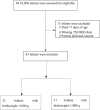
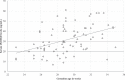
Results: Of the included 83 infants born between November 2016 and March 2018, 44 (53%) had 25(OH)D < 30 ng/mL at birth but achieved vitamin D sufficiency (VDS) by 3 weeks while receiving 120-400 IU/day. Twenty-three (27.7%) infants had at least one 25(OH)D level >100 ng/mL during the study period. Infants whose intake was > 600 IU/day had higher prevalence of vitamin D excess (VDE).
Conclusion: In our study, low 25(OH)D was common in VLBW infants at birth. Vitamin D intake of 120-260 IU/day from parenteral and 200-400 IU/day from enteral route was appropriate for VLBW infants to achieve VDS. Doses > 600 IU/day increased risk of VDE.
© 2021. This is a U.S. government work and not under copyright protection in the U.S.; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Taylor SN, Hollis BW, Wagner CL. Vitamin D needs of preterm infants. NeoReviews. 2009;10:e590–e599. doi: 10.1542/neo.10-12-e590. - DOI
-
- Misra M, Pacaud D, Petryk A, Collett-Solberg PF, Kappy M, Drug and Therapeutics Committee of the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society Vitamin D deficiency in children and its management: review of current knowledge and recommendations. Pediatrics. 2008;122:398–417. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-1894. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

