Human ALS/FTD brain organoid slice cultures display distinct early astrocyte and targetable neuronal pathology
- PMID: 34675437
- PMCID: PMC8553627
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-021-00923-4
Human ALS/FTD brain organoid slice cultures display distinct early astrocyte and targetable neuronal pathology
Abstract
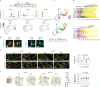
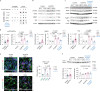
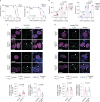
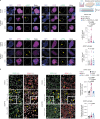
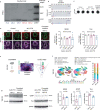
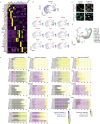
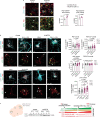
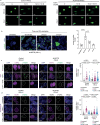
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis overlapping with frontotemporal dementia (ALS/FTD) is a fatal and currently untreatable disease characterized by rapid cognitive decline and paralysis. Elucidating initial cellular pathologies is central to therapeutic target development, but obtaining samples from presymptomatic patients is not feasible. Here, we report the development of a cerebral organoid slice model derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) that recapitulates mature cortical architecture and displays early molecular pathology of C9ORF72 ALS/FTD. Using a combination of single-cell RNA sequencing and biological assays, we reveal distinct transcriptional, proteostasis and DNA repair disturbances in astroglia and neurons. We show that astroglia display increased levels of the autophagy signaling protein P62 and that deep layer neurons accumulate dipeptide repeat protein poly(GA), DNA damage and undergo nuclear pyknosis that could be pharmacologically rescued by GSK2606414. Thus, patient-specific iPSC-derived cortical organoid slice cultures are a reproducible translational platform to investigate preclinical ALS/FTD mechanisms as well as novel therapeutic approaches.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.B. is a co-founder of and consultant for Adrestia Therapeutics Ltd. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




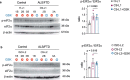
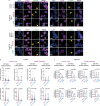
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

