Investigation of the Active Ingredients and Mechanism of Hudi Enteric-Coated Capsules in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis Mice Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification
- PMID: 34675488
- PMCID: PMC8519793
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S326029
Investigation of the Active Ingredients and Mechanism of Hudi Enteric-Coated Capsules in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis Mice Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification
Abstract
Background: Hudi enteric-coated capsule (HDC) is a Chinese medicine prescribed to treat ulcerative colitis (UC). However, its anti-inflammatory active ingredients and mechanisms remain unknown. This study aimed to investigate the active components of HDC and explore its potential mechanisms against UC by integrating network pharmacology and experimental verification.
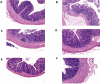
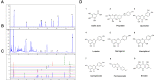
Methods: A DSS-induced colitis murine model was established to validate the efficacy of HDC by detecting disease activity index (DAI) and histopathological changes. Network pharmacological analysis was performed to identify the active compounds and core targets of HDC for the treatment of UC. The main compounds in HDC were identified by high-performance liquid chromatography. The relative expressions of HDC's core targets were also determined in vivo. Finally, molecular docking was applied to model the interaction between HDC and target proteins.
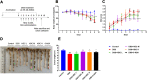
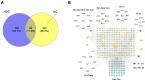
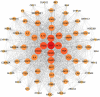
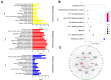
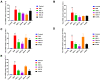
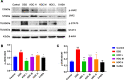
Results: In an in vivo experiment, HDC, especially the middle-dose HDC, effectively reduced clinical symptoms of UC, including weight loss, bloody stool, and colon shortening. Besides, the severity of colitis was considerably suppressed by HDC as evidenced by reduced DAI scores. A total of 118 active compounds and 69 candidate targets from HDC closely related to UC progression were identified via network pharmacology. Enrichment analysis revealed that the key targets of HDC correlated with the expressions of PTGS2, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. Meanwhile, these cytokines were enriched in various biological processes through the IL-17/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. The middle-dose HDC contributed more to ameliorating DSS-induced colitis through this signaling pathway than other dosages. Nine components binding to JAK2, STAT3, IL-17 and IL-6 were identified by molecular docking, confirming again the inhibition effects of HDC on the IL-17/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.
Conclusion: The HDC treatment, particularly the middle-dose, exerted an anti-UC effect in a multi-component, multi-target, and multi-mechanism manner, especially inhibiting the IL-17/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway to downregulate the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: Hudi enteric-coated capsule; IL-17/JAK2/STAT3 pathway; network pharmacology; ulcerative colitis.
© 2021 Ding et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thlaspi arvense suppresses gut microbiota related TNF inflammatory pathway to alleviates ulcerative colitis.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 22;16:1537325. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1537325. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40330488 Free PMC article.
-
Gegen Qinlian decoction relieved DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by modulating Th17/Treg cell homeostasis via suppressing IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling.Phytomedicine. 2021 Apr;84:153519. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153519. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33640781
-
Xiahuo Pingwei San attenuated intestinal inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis mice through inhibiting the receptor for advanced glycation end-products signaling pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2025 Apr;45(2):311-325. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.006. J Tradit Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40151118 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Mechanisms of Bisdemethoxycurcumin in Ulcerative Colitis: Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification.Molecules. 2022 Dec 21;28(1):68. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010068. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical studies of licorice in ulcerative colitis: A systematic review with meta-analysis and network pharmacology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Oct 5;296:115444. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115444. Epub 2022 Jun 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35671864
Cited by
-
Application of network pharmacology in the study of mechanism of Chinese medicine in the treatment of ulcerative colitis: A review.Front Bioinform. 2022 Sep 27;2:928116. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2022.928116. eCollection 2022. Front Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36304327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Animal Experiment to Explore the Efficacy and Potential Mechanism of Baiyu Decoction Against Ulcerative Colitis by Enema.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Nov 23;17:3453-3472. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S432268. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 38024534 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Metagenomics, Network Pharmacology and RNA-Seq Strategies to Reveal the Therapeutic Effects and Mechanisms of Qingchang Wenzhong Decoction on Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Sep 24;18:4273-4289. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S473688. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39347539 Free PMC article.
-
Isatidis Folium Represses Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis and Suppresses the Inflammatory Response by Inhibiting Inflammasome Activation.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 30;16(19):3323. doi: 10.3390/nu16193323. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39408295 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Youhua Kuijie Prescription and sulfasalazine can alleviate experimental colitis via IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 10;15:1437503. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1437503. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39318778 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

