HBV/HIV Coinfection: Impact on the Development and Clinical Treatment of Liver Diseases
- PMID: 34676223
- PMCID: PMC8524435
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.713981
HBV/HIV Coinfection: Impact on the Development and Clinical Treatment of Liver Diseases
Abstract
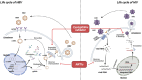
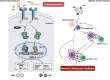
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a common contributor to chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Approximately 10% of people with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) also have chronic HBV co-infection, owing to shared transmission routes. HIV/HBV coinfection accelerates the progression of chronic HBV to cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease, or hepatocellular carcinoma compared to chronic HBV mono-infection. HBV/HIV coinfection alters the natural history of hepatitis B and renders the antiviral treatment more complex. In this report, we conducted a critical review on the epidemiology, natural history, and pathogenesis of liver diseases related to HBV/HIV coinfection. We summarized the novel therapeutic options for these coinfected patients.
Keywords: clinical treatment; coinfection; hepatitis B virus; human immunodeficiency virus; liver disease.
Copyright © 2021 Cheng, Lin and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

