Demographics, Perceptions, and Use of Medical Marijuana among Patients in Florida
- PMID: 34676347
- PMCID: PMC8525215
- DOI: 10.1159/000512342
Demographics, Perceptions, and Use of Medical Marijuana among Patients in Florida
Abstract
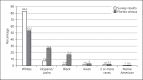
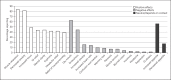
Medical marijuana (MMJ) is currently legal in 35 US states, with an estimated 3.6 million state-legal medical cannabis patients. Although there are currently over 440,000 MMJ patients in the state of Florida, there are limited data on their demographics, reasons and patterns of use, and successes or failures of treatment. The goal of this study is to examine the demographics, perceptions, and use of medical cannabis among patients in Florida, as well as their perceptions of the quality of information received from physicians and dispensaries. One hundred and fifty-seven MMJ patients completed an online survey regarding their characteristics and use. Patients in Florida shared many characteristics with patients in other states, such as race, use frequency, and administration technique. Patients most commonly used MMJ to treat their symptoms of anxiety, pain, and stress and reported great therapeutic effectiveness. A majority (65%) of patients also reported either a reduction or total discontinuation of at least one prescription or over-the-counter drug. The findings highlight the need to further investigate the use of MMJ as a viable treatment for pain and anxiety and to improve access of quality cannabis information to patients, physicians, and dispensary employees.
Keywords: Demographics; Education; Florida; Medical marijuana; Opioids; Survey.
Copyright © 2020 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenthal MS. Drugs: mind, body and society. New York: Oxford University Press; 2018.
-
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine . The health effects of cannabis and cannabinoids. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2017. - PubMed
-
- Kruger DJ, Kruger JS. Medical cannabis users' comparisons between medical cannabis and mainstream medicine. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2019 Jan–Mar;51((1)):31–6. - PubMed
-
- Lucas P, Walsh Z. Medical cannabis access, use, and substitution for prescription opioids and other substances: a survey of authorized medical cannabis patients. Int J Drug Policy. 2017;42:30–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources