Altered increase in STAT1 expression and phosphorylation in severe COVID-19
- PMID: 34676541
- PMCID: PMC8646801
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.202149575
Altered increase in STAT1 expression and phosphorylation in severe COVID-19
Abstract
The interferon pathway, a key antiviral defense mechanism, is being considered as a therapeutic target in COVID-19. Both, substitution of interferon and JAK/STAT inhibition to limit cytokine storms have been proposed. However, little is known about possible abnormalities in STAT signaling in immune cells during SARS-CoV-2 infection. We investigated downstream targets of interferon signaling, including STAT1, STAT2, pSTAT1 and 2, and IRF1, 7 and 9 by flow cytometry in 30 patients with COVID-19, 17 with mild, and 13 with severe infection. We report upregulation of STAT1 and IRF9 in mild and severe COVID-19 cases, which correlated with the IFN-signature assessed by Siglec-1 (CD169) expression on peripheral monocytes. Interestingly, Siglec-1 and STAT1 in CD14+ monocytes and plasmablasts showed lower expression among severe cases compared to mild cases. Contrary to the baseline STAT1 expression, the phosphorylation of STAT1 was enhanced in severe COVID-19 cases, indicating a dysbalanced JAK/STAT signaling that fails to induce transcription of interferon stimulated response elements (ISRE). This abnormality persisted after IFN-α and IFN-γ stimulation of PBMCs from patients with severe COVID-19. Data suggest impaired STAT1 transcriptional upregulation among severely infected patients may represent a potential predictive biomarker and would allow stratification of patients for certain interferon-pathway targeted treatments.
Keywords: COVID-19; IRF9; STAT1; Type I interferon; pSTAT1.
© 2021 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
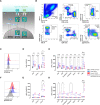


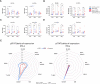
References
-
- Platanias, L. C. , Mechanisms of type‐I‐ and type‐II‐interferon‐mediated signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005. 5: 375–386. - PubMed
-
- Vivier, E. , Tomasello, E. , Baratin, M. , Walzer, T. and Ugolini, S. , Functions of natural killer cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008. 9: 503–510. - PubMed
-
- Bonjardim, C. A. , Interferons (IFNs) are key cytokines in both innate and adaptive antiviral immune responses–and viruses counteract IFN action. Microbes Infect. 2005. 7: 569–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

