A Modern Approach to Dyslipidemia
- PMID: 34676866
- PMCID: PMC9277652
- DOI: 10.1210/endrev/bnab037
A Modern Approach to Dyslipidemia
Abstract
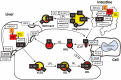
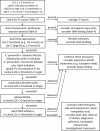
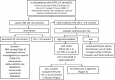
Lipid disorders involving derangements in serum cholesterol, triglycerides, or both are commonly encountered in clinical practice and often have implications for cardiovascular risk and overall health. Recent advances in knowledge, recommendations, and treatment options have necessitated an updated approach to these disorders. Older classification schemes have outlived their usefulness, yielding to an approach based on the primary lipid disturbance identified on a routine lipid panel as a practical starting point. Although monogenic dyslipidemias exist and are important to identify, most individuals with lipid disorders have polygenic predisposition, often in the context of secondary factors such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. With regard to cardiovascular disease, elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is essentially causal, and clinical practice guidelines worldwide have recommended treatment thresholds and targets for this variable. Furthermore, recent studies have established elevated triglycerides as a cardiovascular risk factor, whereas depressed high-density lipoprotein cholesterol now appears less contributory than was previously believed. An updated approach to diagnosis and risk assessment may include measurement of secondary lipid variables such as apolipoprotein B and lipoprotein(a), together with selective use of genetic testing to diagnose rare monogenic dyslipidemias such as familial hypercholesterolemia or familial chylomicronemia syndrome. The ongoing development of new agents-especially antisense RNA and monoclonal antibodies-targeting dyslipidemias will provide additional management options, which in turn motivates discussion on how best to incorporate them into current treatment algorithms.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cholesterol; combined hyperlipidemia; dyslipidemia; lipoprotein(a); triglycerides.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
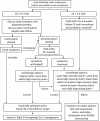
Figures

References
-
- Hegele RA. Plasma lipoproteins: genetic influences and clinical implications. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(2):109-121. - PubMed
-
- Rosenson RS, Brewer HB Jr, Chapman MJ, et al. . HDL measures, particle heterogeneity, proposed nomenclature, and relation to atherosclerotic cardiovascular events. Clin Chem. 2011;57(3):392-410. - PubMed
-
- Altmann SW, Davis HR Jr, Zhu LJ, et al. . Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Science. 2004;303(5661):1201-1204. - PubMed
-
- Sato R, Takano T. Regulation of intracellular cholesterol metabolism. Cell Struct Funct. 1995;20(6):421-427. - PubMed
-
- Kang S, Davis RA. Cholesterol and hepatic lipoprotein assembly and secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1529(1-3):223-230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

