MicroRNA‑200c‑3p suppresses intervertebral disc degeneration by targeting RAP2C/ERK signaling
- PMID: 34676879
- PMCID: PMC8554383
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12505
MicroRNA‑200c‑3p suppresses intervertebral disc degeneration by targeting RAP2C/ERK signaling
Abstract
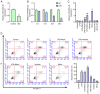
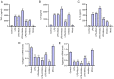
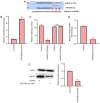
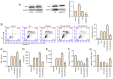
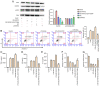
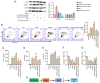
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is a major cause of lower back pain. The high morbidity associated with this disease diminishes the quality of life of those who are affected. MicroRNAs (miRs) play crucial roles in various diseases, including IDD. However, the mechanism via which miR‑200c‑3p plays a role in the development of IDD remains unknown. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of miR‑200c‑3p on the progression of IDD and the underlying mechanism. The expression level of miR‑200c‑3p was evaluated in intervertebral disc tissues from patients with IDD. To construct the IDD cell model, the nucleus pulposus (NP) cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) 24 h following transfection with miR‑200c‑3p mimic or inhibitor. A luciferase activity assay was performed, while reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR and western blotting were conducted to determine the RNA and protein expression levels, respectively. The expression level of miR‑200c‑3p in the intervertebral disc tissues of patients with IDD was lower than that of normal subjects. LPS treatment reduced the expression level of miR‑200c‑3p in NP cells. Moreover, miR‑200c‑3p mimic inhibited LPS‑induced NP cell apoptosis. It was found that miR‑200c‑3p attenuated inflammatory cytokine levels and extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation in NP cells. Furthermore, miR‑200c‑3p targeted Ras‑related protein 2C (RAP2C) in NP cells. RAP2C promoted apoptosis, inflammatory cytokine levels and ECM degradation by activating ERK signaling. Knockdown of RAP2C and inhibition of ERK signaling by SCH772984 partially reversed the proinflammatory effect of the miR‑200c‑3p inhibitor on LPS‑treated NP cells. Thus, miR‑200c‑3p inhibits NP cell apoptosis, inflammatory cytokine levels and ECM degradation in IDD by targeting RAP2C/ERK signaling.
Keywords: ERK signaling; IDD; NP cells; RAP2C; miR‑200c‑3p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang Q, Weng Y, Jiang Y, Zhao S, Zhou D, Xu N. Overexpression of miR-140-5p inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced human intervertebral disc inflammation and degeneration by downregulating toll-like receptor 4. Oncol Rep. 2018;40:793–802. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

