Multi‑faceted role of cancer‑associated adipocytes in the tumor microenvironment (Review)
- PMID: 34676881
- PMCID: PMC8554381
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12506
Multi‑faceted role of cancer‑associated adipocytes in the tumor microenvironment (Review)
Abstract
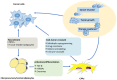
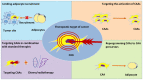
Adipocytes are a type of stromal cell found in numerous different tissues that serve an active role in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer‑associated adipocytes (CAAs) display a malignant phenotype and are found at the invasive tumor front, which mediates the crosstalk network between adipocytes (the precursor cells that will become cancer‑associated adipocytes in the future) and cancer cells. The present review covers the mechanisms of adipocytes in the development of cancer, including metabolic reprogramming, chemotherapy resistance and adipokine regulation. Furthermore, the potential mechanisms involved in the adipocyte‑cancer cell cycle in various types of cancer, including breast, ovarian, colon and rectal cancer, are discussed. Deciphering the complex network of CAA‑cancer cell crosstalk will provide insights into tumor biology and optimize therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: CAA; TME; adipokines; chemotherapy resistance; metabolic reprogramming.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

