A single synonymous nucleotide change impacts the male-killing phenotype of prophage WO gene wmk
- PMID: 34677126
- PMCID: PMC8555981
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67686
A single synonymous nucleotide change impacts the male-killing phenotype of prophage WO gene wmk
Abstract
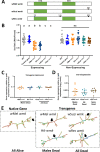
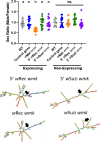
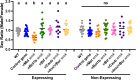
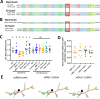
Wolbachia are the most widespread bacterial endosymbionts in animals. Within arthropods, these maternally transmitted bacteria can selfishly hijack host reproductive processes to increase the relative fitness of their transmitting females. One such form of reproductive parasitism called male killing, or the selective killing of infected males, is recapitulated to degrees by transgenic expression of the prophage WO-mediated killing (wmk) gene. Here, we characterize the genotype-phenotype landscape of wmk-induced male killing in D. melanogaster using transgenic expression. While phylogenetically distant wmk homologs induce no sex-ratio bias, closely-related homologs exhibit complex phenotypes spanning no death, male death, or death of all hosts. We demonstrate that alternative start codons, synonymous codons, and notably a single synonymous nucleotide in wmk can ablate killing. These findings reveal previously unrecognized features of transgenic wmk-induced killing and establish new hypotheses for the impacts of post-transcriptional processes in male killing variation. We conclude that synonymous sequence changes are not necessarily silent in nested endosymbiotic interactions with life-or-death consequences.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Wolbachia; genetics; genomics; infectious disease; male killing; microbiology; transgenics.
© 2021, Perlmutter et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JP, SB Is listed as an author on a patent related to the use of wmk in vector control. US Patent 20210000092 16/982708, JM No competing interests declared
Figures
References
-
- Berec L, Maxin D, Bernhauerová V, Rohr J. Male-killing bacteria as agents of insect pest control. Journal of Applied Ecology. 2016;53:1270–1279. doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.12638. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

