Immunotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 34677265
- PMCID: PMC8534845
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol28050347
Immunotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
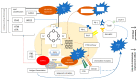
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) remains a poorly understood disease with aggressive features, high relapse rates, and significant morbidity as well as mortality, yet persistently limited treatment options. For three decades, the treatment algorithm of SCLC has been stagnant despite multiple attempts to find alternative therapeutic options that could improve responses and increase survival rates. On the other hand, immunotherapy has been a thriving concept that revolutionized treatment options in multiple malignancies, rendering previously untreatable diseases potentially curable. In extensive stage SCLC, immunotherapy significantly altered the course of disease and is now part of the treatment algorithm in the first-line setting. Nevertheless, the important questions that arise are how best to implement immunotherapy, who would benefit the most, and finally, how to enhance responses.
Keywords: CTLA-4; PD-1; PD-L1; checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Authors confirm that all figures and tables are original and are not replicated from any other source.
Figures
References
-
- Huber R.M., Tufman A. Update on small cell lung cancer management. Breathe. 2012;8:314–330. doi: 10.1183/20734735.013211. - DOI
-
- Micke P., Faldum A., Metz T., Beeh K.M., Bittinger F., Hengstler J.G., Buhl R. Staging small cell lung cancer: Veterans Administration Lung Study Group versus International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer-what limits limited disease? Lung Cancer. 2002;37:271–276. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5002(02)00072-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

