A Review of THz Technologies for Rapid Sensing and Detection of Viruses including SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 34677305
- PMCID: PMC8534088
- DOI: 10.3390/bios11100349
A Review of THz Technologies for Rapid Sensing and Detection of Viruses including SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Virus epidemics such as Ebola virus, Zika virus, MERS-coronavirus, and others have wreaked havoc on humanity in the last decade. In addition, a coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic and its continuously evolving mutants have become so deadly that they have forced the entire technical advancement of healthcare into peril. Traditional ways of detecting these viruses have been successful to some extent, but they are costly, time-consuming, and require specialized human resources. Terahertz-based biosensors have the potential to lead the way for low-cost, non-invasive, and rapid virus detection. This review explores the latest progresses in terahertz technology-based biosensors for the virus, viral particle, and antigen detection, as well as upcoming research directions in the field.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; biosensing; immunobiosensing; metasenors; plasmonics; terahertz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
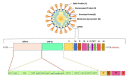
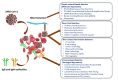
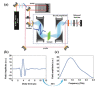

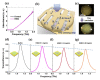
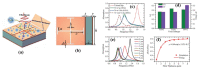
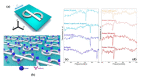
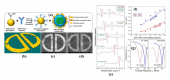
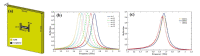
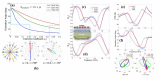
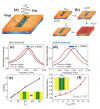
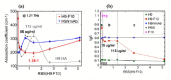
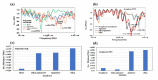
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard | WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. [(accessed on 7 September 2021)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Zhong N.S., Zheng B.J., Li Y.M., Poon L.L.M., Xie Z.H., Chan K.H., Li P.H., Tan S.Y., Chang Q., Xie J.P., et al. Epidemiology and Cause of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People’s Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet. 2003;362:1353–1358. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14630-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

