Knock-In Mice Expressing a 15-Lipoxygenating Alox5 Mutant Respond Differently to Experimental Inflammation Than Reported Alox5-/- Mice
- PMID: 34677413
- PMCID: PMC8538363
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo11100698
Knock-In Mice Expressing a 15-Lipoxygenating Alox5 Mutant Respond Differently to Experimental Inflammation Than Reported Alox5-/- Mice
Abstract
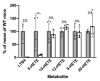
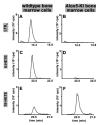
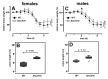
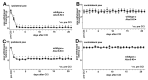
Arachidonic acid 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5) is the key enzyme in the biosynthesis of pro-inflammatory leukotrienes. We recently created knock-in mice (Alox5-KI) which express an arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenating Alox5 mutant instead of the 5-lipoxygenating wildtype enzyme. These mice were leukotriene deficient but exhibited an elevated linoleic acid oxygenase activity. Here we characterized the polyenoic fatty acid metabolism of these mice in more detail and tested the animals in three different experimental inflammation models. In experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), Alox5-KI mice displayed an earlier disease onset and a significantly higher cumulative incidence rate than wildtype controls but the clinical score kinetics were not significantly different. In dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis (DSS) and in the chronic constriction nerve injury model (CCI), Alox5-KI mice performed like wildtype controls with similar genetic background. These results were somewhat surprising since in previous loss-of-function studies targeting leukotriene biosynthesis (Alox5-/- mice, inhibitor studies), more severe inflammatory symptoms were observed in the EAE model but the degree of inflammation in DSS colitis was attenuated. Taken together, our data indicate that these mutant Alox5-KI mice respond differently in two models of experimental inflammation than Alox5-/- animals tested previously in similar experimental setups.
Keywords: eicosanoids; inflammation; leukotrienes; lipoxygenase; pain; resolvins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Functional Characterization of Knock-In Mice Expressing a 12/15-Lipoxygenating Alox5 Mutant Instead of the 5-Lipoxygenating Wild-Type Enzyme.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020 Jan 1;32(1):1-17. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7751. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020. PMID: 31642348
-
Humanization of the Reaction Specificity of Mouse Alox15b Inversely Modified the Susceptibility of Corresponding Knock-In Mice in Two Different Animal Inflammation Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 3;24(13):11034. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311034. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446212 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of pro-inflammatory murine Alox5 into an anti-inflammatory 15S-lipoxygenating enzyme by multiple mutations of sequence determinants.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013 Feb 1;530(1):40-7. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.11.015. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23246375
-
Emerging Roles of 5-Lipoxygenase Phosphorylation in Inflammation and Cell Death.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 29;2019:2749173. doi: 10.1155/2019/2749173. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31871543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-lipoxygenase pathway and its downstream cysteinyl leukotrienes as potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's disease.Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Aug;88:844-855. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.03.022. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Brain Behav Immun. 2020. PMID: 32222525 Review.
Cited by
-
Transgenic mice overexpressing human ALOX15 under the control of the aP2 promoter are partly protected in the complete Freund's adjuvant-induced paw inflammation model.Inflamm Res. 2023 Aug;72(8):1649-1664. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01770-8. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37498393 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the role of tumor-associated ALOX5+ mast cells with transformative function in cervical cancer progression via single-cell RNA sequencing.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 19;15:1434450. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1434450. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39224598 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Chemical Constituents of Miao Ethnomedicine Heiguteng Zhuifeng Huoluo Capsule (HZFC) and the Discovery of Active Substances in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.ACS Omega. 2024 Feb 22;9(9):10860-10874. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09788. eCollection 2024 Mar 5. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38463300 Free PMC article.
-
An integrative analysis of Qingfei Paidu Decoction for its anti-HCoV-229E mechanism in cold and damp environment based on the pharmacokinetics, metabolomics and molecular docking technology.Phytomedicine. 2023 Jan;108:154527. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154527. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36332393 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Roles of Apolipoprotein E4 in Oxidative Lipid Metabolism and Ferroptosis During the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jul 3;74(3):62. doi: 10.1007/s12031-024-02224-4. J Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38958788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

