Fucosterol of Marine Macroalgae: Bioactivity, Safety and Toxicity on Organism
- PMID: 34677444
- PMCID: PMC8539623
- DOI: 10.3390/md19100545
Fucosterol of Marine Macroalgae: Bioactivity, Safety and Toxicity on Organism
Abstract
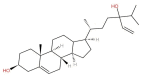
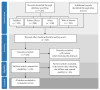
Fucosterol (24-ethylidene cholesterol) is a bioactive compound belonging to the sterol group that can be isolated from marine algae. Fucosterol of marine algae exhibits various biological activities including anti-osteoarthritic, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-photoaging, immunomodulatory, hepatoprotective, anti-neurological, antioxidant, algicidal, anti-obesity, and antimicrobial. Numerous studies on fucosterol, mainly focusing on the quantification and characterization of the chemical structure, bioactivities, and health benefits of fucosterol, have been published. However, there is no comprehensive review on safety and toxicity levels of fucosterol of marine algae. This review aims to discuss the bioactivities, safety, and toxicity of fucosterol comprehensively, which is important for the application and development of fucosterol as a bioactive compound in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical industries. We used four online databases to search for literature on fucosterol published between 2002 and 2020. We identified, screened, selected, and analyzed the literature using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses method and identified 43 studies for review. Despite the potential applications of fucosterol, we identified the need to fill certain related research gaps. Fucosterol exhibited low toxicity in animal cell lines, human cell lines, and animals. However, studies on the safety and toxicity of fucosterol at the clinical stage, which are required before fucosterol is developed for the industry, are lacking.
Keywords: algae; fucosterol; in vitro; in vivo; seaweed; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Heilbron I., Phipers R.F., Wright H.R. The chemistry of the algae. Part I. The algal sterol fucosterol. J. Chem. Soc. 1934:1572–1576. doi: 10.1039/JR9340001572. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

