Investigation of Marine-Derived Natural Products as Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein (RKIP)-Binding Ligands
- PMID: 34677480
- PMCID: PMC8539980
- DOI: 10.3390/md19100581
Investigation of Marine-Derived Natural Products as Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein (RKIP)-Binding Ligands
Abstract
Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) is an essential regulator of the Ras/Raf-1/MEK/ERK signaling cascade and functions by directly interacting with the Raf-1 kinase. The abnormal expression of RKIP is linked with numerous diseases including cancers, Alzheimer's and diabetic nephropathy. Interestingly, RKIP also plays an indispensable role as a tumor suppressor, thus making it an attractive therapeutic target. To date, only a few small molecules have been reported to modulate the activity of RKIP, and there is a need to explore additional scaffolds. In order to achieve this objective, a pharmacophore model was generated that explores the features of locostatin, the most potent RKIP modulator. Correspondingly, the developed model was subjected to screening, and the mapped compounds from Marine Natural Products (MNP) library were retrieved. The mapped MNPs after ensuing drug-likeness filtration were escalated for molecular docking, where locostatin was regarded as a reference. The MNPs exhibiting higher docking scores than locostatin were considered for molecular dynamics simulations, and their binding affinity towards RKIP was computed via MM/PBSA. A total of five molecules revealed significantly better binding free energy scores than compared to locostatin and, therefore, were reckoned as hits. The hits from the present in silico investigation could act as potent RKIP modulators and disrupt interactions of RKIP with its binding proteins. Furthermore, the identification of potent modulators from marine natural habitat can act as a future drug-discovery source.
Keywords: RKIP; binding free energy; marine natural products; molecular docking; molecular dynamics simulations; pharmacophore modeling; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



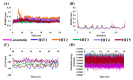


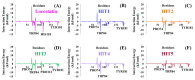
References
-
- Keller E.T., Fu Z., Brennan M. The role of Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) in health and disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004;68:1049–1053. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

