Electrospun Medicated Nanofibers for Wound Healing: Review
- PMID: 34677536
- PMCID: PMC8537333
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes11100770
Electrospun Medicated Nanofibers for Wound Healing: Review
Abstract
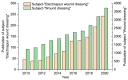
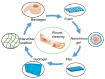
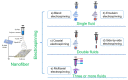
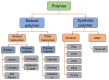
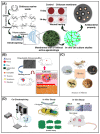
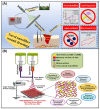
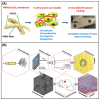
With the increasing demand for wound care and treatment worldwide, traditional dressings have been unable to meet the needs of the existing market due to their limited antibacterial properties and other defects. Electrospinning technology has attracted more and more researchers' attention as a simple and versatile manufacturing method. The electrospun nanofiber membrane has a unique structure and biological function similar to the extracellular matrix (ECM), and is considered an advanced wound dressing. They have significant potential in encapsulating and delivering active substances that promote wound healing. This article first discusses the common types of wound dressing, and then summarizes the development of electrospun fiber preparation technology. Finally, the polymers and common biologically active substances used in electrospinning wound dressings are summarized, and portable electrospinning equipment is also discussed. Additionally, future research needs are put forward.
Keywords: electrospinning; nanocomposite; nanostructure; wound dressing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recent progress of electrospun nanofibers as burning dressings.RSC Adv. 2024 May 1;14(20):14374-14391. doi: 10.1039/d4ra01514b. eCollection 2024 Apr 25. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38694552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes with Various Structures for Wound Dressing.Materials (Basel). 2023 Sep 1;16(17):6021. doi: 10.3390/ma16176021. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospun Medical Sutures for Wound Healing: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Apr 19;14(9):1637. doi: 10.3390/polym14091637. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35566807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Strategies for Diabetic Wound Healing Application.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 5;15(9):2285. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092285. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospun Antibacterial Nanomaterials for Wound Dressings Applications.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Nov 23;11(12):908. doi: 10.3390/membranes11120908. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34940410 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biobran-loaded core/shell nanofibrous scaffold: a promising wound dressing candidate.RSC Adv. 2024 Feb 7;14(7):4930-4945. doi: 10.1039/d3ra08609g. eCollection 2024 Jan 31. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38327812 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress of Electrospun Nanofiber Dressing in the Promotion of Wound Healing.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Sep 13;16(18):2596. doi: 10.3390/polym16182596. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication of Gelatin Nanofibers by Electrospinning-Mixture of Gelatin and Polyvinyl Alcohol.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;14(13):2610. doi: 10.3390/polym14132610. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808656 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Tragopogon graminifolius-loaded electrospun nanofibers and evaluating its wound healing activity in a rat model of skin scar.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 31;16:1533010. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1533010. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39959420 Free PMC article.
-
Electrospinning based biomaterials for biomimetic fabrication, bioactive protein delivery and wound regenerative repair.Regen Biomater. 2024 Dec 3;12:rbae139. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbae139. eCollection 2025. Regen Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39803356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nosrati H., Aramideh Khouy R., Nosrati A., Khodaei M., Banitalebi-Dehkordi M., Ashrafi-Dehkordi K., Sanami S., Alizadeh Z. Nanocomposite scaffolds for accelerating chronic wound healing by enhancing angiogenesis. J. Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19:1–22. doi: 10.1186/s12951-020-00755-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen M., Tian J., Liu Y., Cao H., Li R., Wang J., Wu J., Zhang Q. Dynamic covalent constructed self-healing hydrogel for sequential delivery of antibacterial agent and growth factor in wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2019;373:413–424. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.043. - DOI
-
- Chen K., Wang F., Liu S., Wu X., Xu L., Zhang D. In situ reduction of silver nanoparticles by sodium alginate to obtain silver-loaded composite wound dressing with enhanced mechanical and antimicrobial property. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020;148:501–509. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.156. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

