Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles Labelled with a Lipophilic Dye Using Fluorescence Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
- PMID: 34677545
- PMCID: PMC8539200
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes11100779
Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles Labelled with a Lipophilic Dye Using Fluorescence Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
Abstract
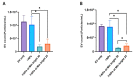
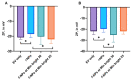
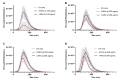
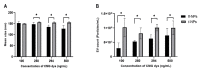
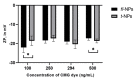
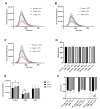
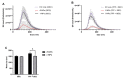
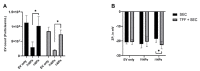
Research on extracellular vesicles (EVs) has intensified over the past decade, including fluorescent membrane labeling of EVs. An optimal fluorescent method requires the size of EVs to be preserved after labeling. Lipophilic fluorescent dyes, such as CellMask™ Green (CMG), have been widely used for this purpose. Here, we investigated conditions affecting the optimum CMG labeling of EVs derived from human choriocarcinoma cells (JAr) and different biological fluids using fluorescence NTA (fl-NTA). The effect of CMG labeling on the size, concentration and zeta potential (ZP) on JAr EVs purified with different methods were measured along with biological fluid-derived EVs. With the increase of CMG dye concentration, a significant decrease in the mean size of fluorescent nanoparticles (fl-NPs) was observed. The ZP of fl-NPs originating from JAr cells with the lowest and highest dye concentrations showed a significant shift towards more and less negative ZP values, respectively. Differences in the concentration of fl-NPs were observed for JAr EVs purified using size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) alone and SEC in combination with tangential flow filtration. The proportion of CMG labeling of NPs varied across different biological sources. CMG labeling may be a reliable technique for the detection of EVs using fl-NTA.
Keywords: NTA; detergent; extracellular vesicles; fluorescence; lipophilic dyes; zeta potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

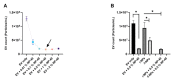
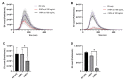
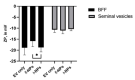
References
-
- Yáñez-Mó M., Siljander P.R.-M., Andreu Z., Zavec A.B., Borràs F.E., Buzas E.I., Buzas K., Casal E., Cappello F., Carvalho J., et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2015;4:27066. doi: 10.3402/jev.v4.27066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

