Quaternized Diaminobutane/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Cross-Linked Membranes for Acid Recovery via Diffusion Dialysis
- PMID: 34677552
- PMCID: PMC8539155
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes11100786
Quaternized Diaminobutane/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Cross-Linked Membranes for Acid Recovery via Diffusion Dialysis
Abstract
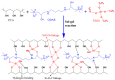
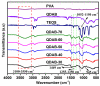
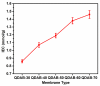
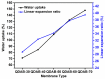
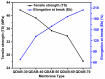
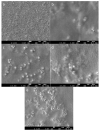
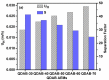
Diffusion dialysis (DD) using anion exchange membranes (AEM) is an effective process for acid recovery and requires the preparation of suitable materials for AEMs, characterized by unique ions transport properties. In this work, novel AEMs composed of quaternized diaminobutane (QDAB) and poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) were cross-linked by tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) via the sol-gel process. The prepared AEMs were systematically characterized by Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, ion-exchange capacity (IEC) analysis, thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA), water uptake, linear expansion ratio (LER), and mechanical strength determination, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and DD performance analysis for acid recovery using a hydrochloric acid/iron chloride (HCl/FeCl2) aqueous mixture and varying the QDAB content. The prepared AEMs exhibited IEC values between 0.86 and 1.46 mmol/g, water uptake values within 71.3 and 47.8%, moderate thermal stability, tensile strength values in the range of 26.1 to 41.7 MPa, and elongation from 68.2 to 204.6%. The dialysis coefficient values were between 0.0186 and 0.0295 m/h, whereas the separation factors range was 24.7-44.1 at 25 °C. The prepared membranes have great potential for acid recovery via diffusion dialysis.
Keywords: PVA; TEOS cross-linked; acid recovery; anion exchange membrane; diffusion dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Du X., Wang Z., Zhang H., Yuan Y., Wang H., Zhang Z. Prepared poly(aryl piperidinium) anion exchange membranes for acid recovery to improve dialysis coefficients and selectivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2021;619:118805. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118805. - DOI
-
- Huang X., Xu Y., Shan C., Li X., Zhang W., Pan B. Coupled Cu(II)-EDTA degradation and Cu(II) removal from acidic wastewater by ozonation: Performance, products and pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2016;299:23–29. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.044. - DOI
-
- Ji W., Wu B., Zhu Y., Irfan M., Afsar N.U., Ge L., Xu T. Self-organized nanostructured anion exchange membranes for acid recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2020;382:122838. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122838. - DOI
-
- Xiao H.F., Chen Q., Cheng H., Li X.M., Qin W.M., Chen B.S., Xiao D., Zhang W.M. Selective removal of halides from spent zinc sulfate electrolyte by diffusion dialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2017;537:111–118. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2017.05.009. - DOI
-
- San Román M.F., Ortiz-Gándara I., Bringas E., Ibañez R., Ortiz I. Membrane selective recovery of HCl, zinc and iron from simulated mining effluents. Desalination. 2018;440:78–87. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2018.02.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

