The Hsp70-Hsp90 go-between Hop/Stip1/Sti1 is a proteostatic switch and may be a drug target in cancer and neurodegeneration
- PMID: 34677645
- PMCID: PMC8629791
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-021-03962-z
The Hsp70-Hsp90 go-between Hop/Stip1/Sti1 is a proteostatic switch and may be a drug target in cancer and neurodegeneration
Abstract
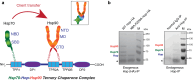
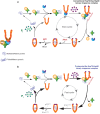
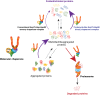
The Hsp70 and Hsp90 molecular chaperone systems are critical regulators of protein homeostasis (proteostasis) in eukaryotes under normal and stressed conditions. The Hsp70 and Hsp90 systems physically and functionally interact to ensure cellular proteostasis. Co-chaperones interact with Hsp70 and Hsp90 to regulate and to promote their molecular chaperone functions. Mammalian Hop, also called Stip1, and its budding yeast ortholog Sti1 are eukaryote-specific co-chaperones, which have been thought to be essential for substrate ("client") transfer from Hsp70 to Hsp90. Substrate transfer is facilitated by the ability of Hop to interact simultaneously with Hsp70 and Hsp90 as part of a ternary complex. Intriguingly, in prokaryotes, which lack a Hop ortholog, the Hsp70 and Hsp90 orthologs interact directly. Recent evidence shows that eukaryotic Hsp70 and Hsp90 can also form a prokaryote-like binary chaperone complex in the absence of Hop, and that this binary complex displays enhanced protein folding and anti-aggregation activities. The canonical Hsp70-Hop-Hsp90 ternary chaperone complex is essential for optimal maturation and stability of a small subset of clients, including the glucocorticoid receptor, the tyrosine kinase v-Src, and the 26S/30S proteasome. Whereas many cancers have increased levels of Hop, the levels of Hop decrease in the aging human brain. Since Hop is not essential in all eukaryotic cells and organisms, tuning Hop levels or activity might be beneficial for the treatment of cancer and neurodegeneration.
Keywords: Aggregation; Aging; Degradation; Molecular chaperone; Proteasome; Protein folding; Proteostasis; Stress response.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Hsp70-Hsp90 co-chaperone Hop/Stip1 shifts the proteostatic balance from folding towards degradation.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 25;11(1):5975. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19783-w. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33239621 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of hippocampal neuronal resilience during aging by the Hsp70/Hsp90 co-chaperone STI1.J Neurochem. 2020 Jun;153(6):727-758. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14882. Epub 2019 Oct 31. J Neurochem. 2020. PMID: 31562773
-
Stress-inducible phosphoprotein 1 (Sti1/Stip1/Hop) sequesters misfolded proteins during stress.FEBS J. 2025 Jul;292(14):3634-3658. doi: 10.1111/febs.17389. Epub 2024 Dec 30. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 39739753 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into Sti1/Hop's cochaperone function highlight the complexity of proteostatic regulation.FEBS J. 2025 Jul;292(14):3629-3633. doi: 10.1111/febs.70108. Epub 2025 Apr 21. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 40259657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hsp70/Hsp90 Organising Protein (Hop): Coordinating Much More than Chaperones.Subcell Biochem. 2023;101:81-125. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-14740-1_3. Subcell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36520304 Review.
Cited by
-
Translational reprogramming in response to accumulating stressors ensures critical threshold levels of Hsp90 for mammalian life.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 21;13(1):6271. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33916-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36270993 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock protein 90: biological functions, diseases, and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jan 25;5(2):e470. doi: 10.1002/mco2.470. eCollection 2024 Feb. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38283176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JAK2-Mediated Phosphorylation of Stress-Induced Phosphoprotein-1 (STIP1) in Human Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 22;23(5):2420. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052420. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269562 Free PMC article.
-
The Plasmodium falciparum exported J domain proteins fine-tune human and malarial Hsp70s: pathological exploitation of proteostasis machinery.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jun 30;10:1216192. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1216192. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37457831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat shock protein 70 enhances viral replication by stabilizing Senecavirus A nonstructural proteins L and 3D.Vet Res. 2024 Dec 18;55(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01414-7. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39695881 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

