In silico identification of A1 agonists and A2a inhibitors in pain based on molecular docking strategies and dynamics simulations
- PMID: 34677752
- PMCID: PMC9984648
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-021-09808-4
In silico identification of A1 agonists and A2a inhibitors in pain based on molecular docking strategies and dynamics simulations
Abstract
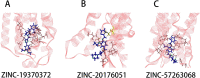
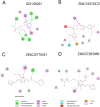
Most recently, the adenosine is considered as one of the most promising targets for treating pain, with few side effects. It exists in the central nervous system, and plays a key role in nociceptive afferent pathway. It is reported that the A1 receptor (A1R) could inhibit Ca2+ channels to reduce the pain like analgesic mechanism of morphine. And, A2a receptor (A2aR) was reported to enhance the accumulation of AMP (cAMP) and released peptides from sensory neurons, resulting in constitutive activation of pain. Much evidence showed that A1R and A2aR could be served as the interesting targets for the treatment of pain. Herein, virtual screening was utilized to identify the small molecule compounds towards A1R and A2aR, and top six molecules were considered as candidates via amber scores. The molecular dynamic (MD) simulations and molecular mechanics/generalized born surface area (MM/GBSA) were employed to further analyze the affinity and binding stability of the six molecules towards A1R and A2aR. Moreover, energy decomposition analysis showed significant residues in A1R and A2aR, including His1383, Phe1276, and Glu1277. It provided basics for discovery of novel agonists and antagonists. Finally, the agonists of A1R (ZINC19943625, ZINC13555217, and ZINC04698406) and inhibitors of A2aR (ZINC19370372, ZINC20176051, and ZINC57263068) were successfully recognized. Taken together, our discovered small molecules may serve as the promising candidate agents for future pain research.
Keywords: Adenosine A1 receptor; Adenosine A2a receptor; Drug discovery; Pain; Potential agents.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in the article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative Study of Receptor-, Receptor State-, and Membrane-Dependent Cholesterol Binding Sites in A2A and A1 Adenosine Receptors Using Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulations.J Chem Inf Model. 2023 Feb 13;63(3):928-949. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c01181. Epub 2023 Jan 13. J Chem Inf Model. 2023. PMID: 36637988
-
The antidepressant-like effect of guanosine involves the modulation of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Jun;19(2):387-399. doi: 10.1007/s11302-022-09898-8. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 36166131 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of cAMP-PKA pathway in adenosine A1 and A2A receptor-mediated regulation of acetaldehyde-induced activation of HSCs.Biochimie. 2015 Aug;115:59-70. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.04.019. Epub 2015 May 6. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25956975
-
Adenosine A1 and A2A Receptors in the Brain: Current Research and Their Role in Neurodegeneration.Molecules. 2017 Apr 23;22(4):676. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040676. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28441750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel approaches for targeting the adenosine A2A receptor.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2015 Jan;10(1):63-80. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2015.971006. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 25311639 Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Molecular Docking Analysis of Karanjin against Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases as a Potential Natural Lead Molecule for New Drug Design, Development and Therapy.Molecules. 2022 Apr 29;27(9):2834. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092834. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566187 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Purinergic signalling - a perspective from China.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):1-3. doi: 10.1007/s11302-022-09914-x. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 36515791 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

