Computer vision reveals hidden variables underlying NF-κB activation in single cells
- PMID: 34678061
- PMCID: PMC8535821
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg4135
Computer vision reveals hidden variables underlying NF-κB activation in single cells
Abstract
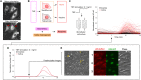
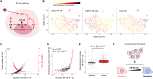
Individual cells are heterogeneous when responding to environmental cues. Under an external signal, certain cells activate gene regulatory pathways, while others completely ignore that signal. Mechanisms underlying cellular heterogeneity are often inaccessible because experiments needed to study molecular states destroy the very states that we need to examine. Here, we developed an image-based support vector machine learning model to uncover variables controlling activation of the immune pathway nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). Computer vision analysis predicts the identity of cells that will respond to cytokine stimulation and shows that activation is predetermined by minute amounts of “leaky” NF-κB (p65:p50) localization to the nucleus. Mechanistic modeling revealed that the ratio of NF-κB to inhibitor of NF-κB predetermines leakiness and activation probability of cells. While cells transition between molecular states, they maintain their overall probabilities for NF-κB activation. Our results demonstrate how computer vision can find mechanisms behind heterogeneous single-cell activation under proinflammatory stimuli.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The NF-κB p65 and p50 homodimer cooperate with IRF8 to activate iNOS transcription.BMC Cancer. 2015 Oct 23;15:770. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1808-6. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26497740 Free PMC article.
-
Resolution of inflammation: prostaglandin E2 dissociates nuclear trafficking of individual NF-kappaB subunits (p65, p50) in stimulated rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts.J Immunol. 2005 Nov 15;175(10):6924-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.10.6924. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16272352
-
The p50-p50 NF-kappaB complex as a stimulus-specific repressor of gene activation.Mol Cell Biochem. 2004 Oct;265(1-2):171-83. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000044394.66951.4d. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15543947
-
Analysis and quantitation of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation in tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) activated vascular endothelial cells.Microsc Microanal. 2006 Jun;12(3):269-76. doi: 10.1017/S1431927606060260. Microsc Microanal. 2006. PMID: 17481363
-
Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:621-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.621. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10837071 Review.
Cited by
-
Live-cell imaging reveals single-cell and population-level infection strategies of Listeria monocytogenes in macrophages.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 22;14:1235675. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1235675. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37675103 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of IκB⍺ modulates NF-κB activation of inflammatory target gene expression.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 May 9;10:1187187. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1187187. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37228587 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous NF-κB activation and enhancer features shape transcription in Drosophila immunity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 19:2025.05.19.654881. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.19.654881. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40475619 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Post-transcriptional regulatory feedback encodes JAK-STAT signal memory of interferon stimulation.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 27;13:947213. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.947213. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36238296 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of Cellular Nrf2/NF-κB Signalling after Plasma Stimulation of Malignant vs. Non-Malignant Dermal Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10967. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010967. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elowitz M. B., Levine A. J., Siggia E. D., Swain P. S., Stochastic gene expression in a single cell. Science 297, 1183–1186 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Ben-David U., Siranosian B., Ha G., Tang H., Oren Y., Hinohara K., Strathdee C. A., Dempster J., Lyons N. J., Burns R., Nag A., Kugener G., Cimini B., Tsvetkov P., Maruvka Y. E., O’Rourke R., Garrity A., Tubelli A. A., Bandopadhayay P., Tsherniak A., Vazquez F., Wong B., Birger C., Ghandi M., Thorner A. R., Bittker J. A., Meyerson M., Getz G., Beroukhim R., Golub T. R., Genetic and transcriptional evolution alters cancer cell line drug response. Nature 560, 325–330 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

