Intracellular receptor EPAC regulates von Willebrand factor secretion from endothelial cells in a PI3K-/eNOS-dependent manner during inflammation
- PMID: 34678311
- PMCID: PMC8526113
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101315
Intracellular receptor EPAC regulates von Willebrand factor secretion from endothelial cells in a PI3K-/eNOS-dependent manner during inflammation
Abstract
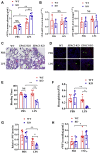
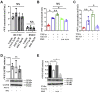
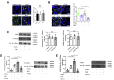
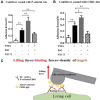
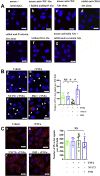
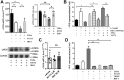
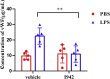
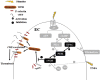
Coagulopathy is associated with both inflammation and infection, including infections with novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2, the causative agent Coagulopathy is associated with both inflammation and infection, including infection with novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2, the causative agent of COVID-19. Clot formation is promoted via cAMP-mediated secretion of von Willebrand factor (vWF), which fine-tunes the process of hemostasis. The exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC) is a ubiquitously expressed intracellular cAMP receptor that plays a regulatory role in suppressing inflammation. To assess whether EPAC could regulate vWF release during inflammation, we utilized our EPAC1-null mouse model and revealed increased secretion of vWF in endotoxemic mice in the absence of the EPAC1 gene. Pharmacological inhibition of EPAC1 in vitro mimicked the EPAC1-/- phenotype. In addition, EPAC1 regulated tumor necrosis factor-α-triggered vWF secretion from human umbilical vein endothelial cells in a manner dependent upon inflammatory effector molecules PI3K and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Furthermore, EPAC1 activation reduced inflammation-triggered vWF release, both in vivo and in vitro. Our data delineate a novel regulatory role for EPAC1 in vWF secretion and shed light on the potential development of new strategies to control thrombosis during inflammation.
Keywords: AFM; EPAC; PI3K; Weibel–Palade body; eNOS; endothelial cell; inflammation; spatial proximity; von Willebrand factor secretion.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Update of
-
EPAC regulates von Willebrand factor secretion from endothelial cells in a PI3K/eNOS-dependent manner during inflammation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Sep 4:2020.09.04.282806. doi: 10.1101/2020.09.04.282806. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2021 Nov;297(5):101315. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101315. PMID: 32908983 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
EPAC regulates von Willebrand factor secretion from endothelial cells in a PI3K/eNOS-dependent manner during inflammation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Sep 4:2020.09.04.282806. doi: 10.1101/2020.09.04.282806. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2021 Nov;297(5):101315. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101315. PMID: 32908983 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Forskolin increases angiogenesis through the coordinated cross-talk of PKA-dependent VEGF expression and Epac-mediated PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling.Cell Signal. 2009 Jun;21(6):906-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.01.038. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 19385062
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate-dependent Rac exchange factor 1 regulates epinephrine-induced exocytosis of Weibel-Palade bodies.J Thromb Haemost. 2014 Feb;12(2):273-81. doi: 10.1111/jth.12460. J Thromb Haemost. 2014. PMID: 24283667
-
von Willebrand factor and inflammation.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jul;15(7):1285-1294. doi: 10.1111/jth.13696. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28671350 Review.
-
The Manifold Cellular Functions of von Willebrand Factor.Cells. 2021 Sep 8;10(9):2351. doi: 10.3390/cells10092351. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572000 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of SARS-CoV-2 proteins on vascular permeability.Elife. 2021 Oct 25;10:e69314. doi: 10.7554/eLife.69314. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34694226 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Associated Increase in Thrombogenicity and Its Correlation with von Willebrand Factor.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 16;10(18):4190. doi: 10.3390/jcm10184190. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34575297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein-Induced Endothelial Cell Permeability and vWF Secretion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 16;24(6):5664. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065664. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982738 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

