The effects of dietary saturated fat source on weight gain and adiposity are influenced by both sex and total dietary lipid intake in zebrafish
- PMID: 34679092
- PMCID: PMC8535427
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257914
The effects of dietary saturated fat source on weight gain and adiposity are influenced by both sex and total dietary lipid intake in zebrafish
Abstract
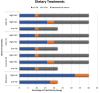
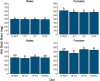
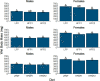
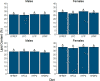
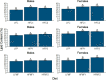
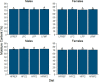
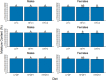
The effects of saturated fat intake on obesity and cardiovascular health remain inconclusive, likely due in part to their varied nature and interactions with other nutrients. Investigating the synergistic effects of different saturated fat sources with other dietary lipid components will help establish more accurate nutritional guidelines for dietary fat intake. Over the past two decades, zebrafish (Danio rerio) have been established as an attractive model system to address questions regarding contributions of dietary lipid intake to diet-induced obesity in humans. The goal of the present study was to assess interactions of three different saturated fat sources (milk fat, palm oil, and coconut oil) with sex and total dietary lipid intake on weight gain and body composition in adult zebrafish. Larvae were raised on live feeds until 28 days post fertilization, and then fed a formulated maintenance diet until three months of age. An eight-week feeding trial was then initiated, in which zebrafish were fed nine experimental low- and high-fat diets varying in saturated fatty acid and long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid content, in addition to a low-fat and high-fat control diet. At termination of the feeding trial, each treatment was evaluated according to body mass, moisture content, and adiposity. Sex and diet significantly interacted in their effects on body mass (P = 0.026), moisture content (P = 0.044), and adiposity (P = 0.035). The influence of saturated fat source on body mass was observed to be dependent on intake of total dietary lipid. In females, all three saturated fat sources had similar effects on adiposity. From these observations, we hypothesize that impacts of saturated fat intake on energy allocation and obesity-related phenotypes are influenced by both sex and intake of other dietary lipid components. Our results suggest that current nutritional guidelines for saturated fat intake may need to be re-evaluated and take sex-specific recommendations into consideration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

