Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease in the Era of Disease-Modifying Treatments
- PMID: 34679323
- PMCID: PMC8534246
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci11101258
Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease in the Era of Disease-Modifying Treatments
Abstract
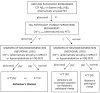
Correct in vivo diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) helps to avoid administration of disease-modifying treatments in non-AD patients, and allows the possible use of such treatments in clinically atypical AD patients. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers offer a tool for AD diagnosis. A reduction in CSF β-amyloid (marker of amyloid plaque burden), although compatible with Alzheimer's pathological change, may also be observed in other dementing disorders, including vascular cognitive disorders due to subcortical small-vessel disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Thus, for the diagnosis of AD, an abnormal result of CSF β-amyloid may not be sufficient, and an increase in phospho-tau (marker of tangle pathology) is also required in order to confirm AD diagnosis in patients with a typical amnestic presentation and reveal underlying AD in patients with atypical or mixed and diagnostically confusing clinical presentations.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; aducanumab; anti-amyloid antibodies; beta amyloid; biomarkers; cerebrospinal fluid; phospho-tau.
Conflict of interest statement
G.P.P. receives fees from Biogen International as a consultant of advisory board. E.K. has none.
Figures
Similar articles
-
From Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurochemistry to Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease in the Era of Anti-Amyloid Treatments. Report of Four Patients.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 2;9(10):1376. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101376. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680493 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) beta-amyloid (1-42), phosphorylated tau (ptau-181) and total Tau protein in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other dementia at Siriraj Hospital, Thailand.J Med Assoc Thai. 2011 Feb;94 Suppl 1:S77-83. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011. PMID: 21721431
-
Cerebrospinal fluid tau and amyloid-β1-42 in patients with dementia.Brain. 2015 Sep;138(Pt 9):2716-31. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv181. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Brain. 2015. PMID: 26133663
-
Clinical indications for analysis of Alzheimer's disease CSF biomarkers.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2013 Oct;169(10):709-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2013.07.024. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2013. PMID: 24016466 Review.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus versus Alzheimer's Disease and Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease: A Systematic Review.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;68(1):267-279. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180816. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 30741681
Cited by
-
The Role of Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Dementia and Other Related Neurodegenerative Disorders.Brain Sci. 2022 May 11;12(5):627. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12050627. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35625013 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Classical Biomarker Levels in Mixed vs. Pure A+T+ (A+T1+) Alzheimer's Disease.Biomedicines. 2024 Dec 20;12(12):2904. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122904. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767810 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome-wide association studies using summary pQTL data of brain, CSF, and plasma identify 30 risk genes of Alzheimer's disease dementia.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Jun 18;17(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01774-y. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40533815 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting association pattern of plasma low-density lipoprotein with white matter integrity in APOE4 carriers versus non-carriers.Neurobiol Aging. 2024 Nov;143:41-52. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2024.08.005. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Neurobiol Aging. 2024. PMID: 39213809
-
Critical Factors in Sample Collection and Preparation for Clinical Metabolomics of Underexplored Biological Specimens.Metabolites. 2024 Jan 5;14(1):36. doi: 10.3390/metabo14010036. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38248839 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jellinger K.A., Bancher C. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease: A critical update. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1998;54:77–95. - PubMed
-
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E.M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology. 1984;34:939–944. doi: 10.1212/WNL.34.7.939. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lopez O.L., Becker J.T., Klunk W., Saxton J., Hamilton R.L., Kaufer D.I., Sweet R.A., Cidis Meltzer C., Wisniewski S., Kamboh M.I., et al. Research evaluation and diagnosis of probable Alzheimer’s disease over the last two decades: I. Neurology. 2000;55:1854–1862. doi: 10.1212/WNL.55.12.1854. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsantzali I., Paraskevas P.G., Paraskevas S.G., Efthimiopoulos S., Tsivgoulis G., Paraskevas G.P. Atypical presentations of Alzheimer’s disease: Beyond amnestic dementia. Clin. Exp. Investig. 2020;1:2–4. doi: 10.31487/j.CEI.2020.03.03. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources