The Natural Products Targeting on Allergic Rhinitis: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Drug Discovery
- PMID: 34679659
- PMCID: PMC8532887
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10101524
The Natural Products Targeting on Allergic Rhinitis: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Drug Discovery
Abstract
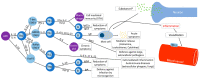
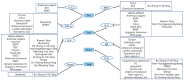
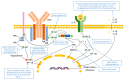
More than 500 million people suffer from allergic rhinitis (AR) in the world. Current treatments include oral antihistamines and intranasal corticosteroids; however, they often cause side effects and are unsuitable for long-term exposure. Natural products could work as a feasible alternative, and this study aimed to review the efficacies and mechanisms of natural substances in AR therapies by examining previous literature. Fifty-seven studies were collected and classified into plants, fungi, and minerals decoction; clinical trials were organized separately. The majority of the natural products showed their efficacies by two mechanisms: anti-inflammation regulating diverse mediators and anti-oxidation controlling the activity of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB) pathway stimulated by reactive oxygen species (ROS). The main AR factors modified by natural products included interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, IL-13, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), and phospho-ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2). Although further studies are required to verify their efficacies and safeties, natural products can significantly contribute to the treatment of AR.
Keywords: allergic rhinitis; antioxidants; inflammation; interleukin; natural products; nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Brożek J.L., Bousquet J., Agache I., Agarwal A., Bachert C., Bosnic-Anticevich S., Brignardello-Petersen R., Canonica G.W., Casale T., Chavannes N.H. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines—2016 revision. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017;140:950–958. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.03.050. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

