EGFR Exon 20 Insertion in Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Survival and Clinical Efficacy of EGFR Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitor and Chemotherapy
- PMID: 34680280
- PMCID: PMC8534282
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13205132
EGFR Exon 20 Insertion in Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Survival and Clinical Efficacy of EGFR Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitor and Chemotherapy
Abstract
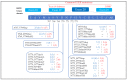
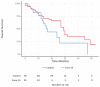
EGFR exon 20 insertions are rare genetic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) that are usually unresponsive to approved EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). In this paper, we describe the clinical characteristics, efficacy of EFGR TKIs and chemotherapy, and resulting survival in this population. We retrospectively collected patients with EGFR exon 20 insertions (Exon20ins) from 11 French genetic platforms and paired them (1:2 ratio) with classic Exon 19/21 EGFR mutation patients (controls). Between 2012 and 2017, 35 Exon20ins patients were included. These patients were younger at diagnosis than the controls. All Exon20ins patients who were treated with first-line EGFR TKIs (n = 6) showed progressive disease as the best tumor response. There was no significant difference in the tumor response or the disease control rate with first-line platinum-based chemotherapy between the two groups. A trend towards shorter overall survival was observed in Exon20ins vs. controls (17 months (14-not reach(NR) 95% confidence interval(CI) vs. 29 months (17-NR 95%CI), p = 0.09), respectively. A significant heterogeneity in amino acid insertion in EGFR exon 20 was observed. EGFR exon 20 insertions are heterogeneous molecular alterations in NSCLC that are resistant to classic EGFR TKIs, which contraindicates their use as a first-line treatment.
Keywords: EGFR; NSCLC; TKI; chemotherapy; exon 20 insertion; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barlesi F., Mazières J., Merlio J.-P., Debieuvre D., Mosser J., Léna H., Ouafik L., Besse B., Rouquette I., Westeel V., et al. Routine Molecular Profiling of Cancer: Results of a One-Year Nationwide Program of the French Cooperative Thoracic Intergroup (IFCT) for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients. Lancet. 2016;287:1415–1426. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00004-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Riess J., Gandare D., Frampton J., Madison R., Peled N., Bufill J., Dy G., Ou S., Stephens P., McPherson J., et al. Diverse EGFR Exon 20 Insertions and Co-Occurring Molecular Alterations Identified by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018;13:1560–1568. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.06.019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cerami E., Gao J., Dogrusoz U., Gross B.E., Sumer S.O., Aksoy B.A., Jacobsen A., Byrne C.J., Heuer M.L., Larsson E., et al. The CBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:401–404. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

