T-Cadherin and the Ratio of Its Ligands as Predictors of Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 34680515
- PMCID: PMC8533356
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9101398
T-Cadherin and the Ratio of Its Ligands as Predictors of Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Pilot Study
Abstract
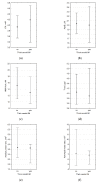
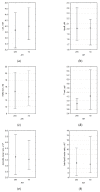
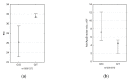
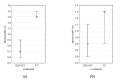
In the cardiovascular system, atherogenic low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and the protective hormone adiponectin bind to the same receptor, T-cadherin. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that the ratio of circulating LDL to high-molecular weight (HMW) adiponectin could predict the development of atherosclerosis. Using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, we measured the level of circulating HMW adiponectin in the blood of donors together with ultrasound measuring of intima-media thickness (IMT) of carotid arteries. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the T-cadherin gene were identified using polymerase chain reaction. We found that carotid artery IMT is inversely correlated with the level of HMW in male subjects. We also found that the G allele of rs12444338 SNP in the T-cadherin gene correlates with a lower level of circulating T-cadherin and thinner IMT and therefore could be considered as an atheroprotective genotype. Despite our data, we could not provide direct evidence for the initial study hypothesis. However, we did uncover an important correlation between circulating T-cadherin and thinner carotid IMT.
Keywords: T-cadherin; atherosclerosis; high molecular weight adiponectin; intima-media thickness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Bochkov V.N., Kuz’menko E.S., Rezink T., Tkachuk V.A. “Classical” apo B,E-receptor does not mediate the activating effect of low density lipoproteins on the second messenger system in human platelets and vascular smooth muscle cells. Biokhimiia. 1994;59:1330–1339. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

