Mechanisms, Pathophysiology and Currently Proposed Treatments of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 34681202
- PMCID: PMC8539950
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14100979
Mechanisms, Pathophysiology and Currently Proposed Treatments of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
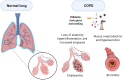
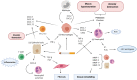
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is one of the leading global causes of morbidity and mortality. A hallmark of COPD is progressive airflow obstruction primarily caused by cigarette smoke (CS). CS exposure causes an imbalance favoring pro- over antioxidants (oxidative stress), leading to transcription factor activation and increased expression of inflammatory mediators and proteases. Different cell types, including macrophages, epithelial cells, neutrophils, and T lymphocytes, contribute to COPD pathophysiology. Alteration in cell functions results in the generation of an oxidative and inflammatory microenvironment, which contributes to disease progression. Current treatments include inhaled corticosteroids and bronchodilator therapy. However, these therapies do not effectively halt disease progression. Due to the complexity of its pathophysiology, and the risk of exacerbating symptoms with existing therapies, other specific and effective treatment options are required. Therapies directly or indirectly targeting the oxidative imbalance may be promising alternatives. This review briefly discusses COPD pathophysiology, and provides an update on the development and clinical testing of novel COPD treatments.
Keywords: COPD; chronic obstructive pulmonary dysfunction; current treatments; pathophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- GOLD Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2021 Repost. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease—GOLD. 2021. [(accessed on 30 August 2021)]. Available online: https://goldcopd.org/2021-gold-reports/
-
- Halpin D.M.G., Celli B.R., Criner G.J., Frith P., Varela M.V.L., Salvi S., Vogelmeier C.F., Chen R., Mortimer K., De Oca M.M., et al. The GOLD Summit on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in low- and middle-income countries. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2019;23:1131–1141. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.19.0397. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 001/Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- E-26/010.000983/2019/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- E26/203.290/2017/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- 401700/2020-8/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- E-26/210.181/2020/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

