Experimental Evaluation of Food-Grade Semi-Refined Carrageenan Toxicity
- PMID: 34681837
- PMCID: PMC8539956
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222011178
Experimental Evaluation of Food-Grade Semi-Refined Carrageenan Toxicity
Abstract
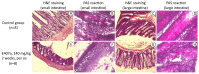
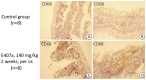
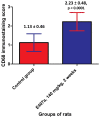
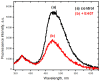
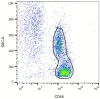
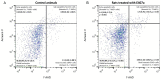
The safety of food additives E407 and E407a has raised concerns in the scientific community. Thus, this study aims to assess the local and systemic toxic effects of the common food additive E407a in rats orally exposed to it for two weeks. Complex evaluations of the effects of semi-refined carrageenan (E407a) on rats upon oral exposure were performed. Local effects of E407a on the intestine were analyzed using routine histological stains and CD68 immunostaining. Furthermore, circulating levels of inflammatory markers were assessed. A fluorescent probe O1O (2- (2'-OH-phenyl)-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazole) was used for evaluating the state of leukocyte cell membranes. Cell death modes of leukocytes were analyzed by flow cytometry using Annexin V and 7-aminoactinomycin D staining. Oral administration of the common food additive E407a was found to be associated with altered small and large intestinal morphology, infiltration of the lamina propria in the small intestine with macrophages (CD68+ cells), high systemic levels of inflammation markers, and changes in the lipid order of the phospholipid bilayer in the cell membranes of leukocytes, alongside the activation of their apoptosis. Our findings suggest that oral exposure to E407a through rats results in the development of intestinal inflammation.
Keywords: E407a; animal model; carrageenan; fluorescent probe; inflammation; intestine; leukocytes; processed Eucheuma seaweed; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of semi-refined carrageenan (food additive E407a) on cell membranes of leukocytes assessed in vivo and in vitro.Med Glas (Zenica). 2021 Feb 1;18(1):176-183. doi: 10.17392/1213-21. Med Glas (Zenica). 2021. PMID: 33078914
-
Semi-refined carrageenan promotes generation of reactive oxygen species in leukocytes of rats upon oral exposure but not in vitro.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2021 Mar;171(3-4):68-78. doi: 10.1007/s10354-020-00786-7. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2021. PMID: 33108805
-
Food additive E407a stimulates eryptosis in a dose-dependent manner.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2021 Aug 12. doi: 10.1007/s10354-021-00874-2. Online ahead of print. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2021. PMID: 34383224
-
A critical review of the toxicological effects of carrageenan and processed eucheuma seaweed on the gastrointestinal tract.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2002 Sep;32(5):413-44. doi: 10.1080/20024091064282. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 12389870 Review.
-
Evidence and hypotheses on adverse effects of the food additives carrageenan (E 407)/processed Eucheuma seaweed (E 407a) and carboxymethylcellulose (E 466) on the intestines: a scoping review.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2023 Dec;53(9):521-571. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2023.2270574. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 38032203
Cited by
-
Carrageenan: structure, properties and applications with special emphasis on food science.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 27;15(27):22035-22062. doi: 10.1039/d5ra03296b. eCollection 2025 Jun 23. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40584756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Developments and Formulations for Hydrophobic Modification of Carrageenan Bionanocomposites.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Mar 26;15(7):1650. doi: 10.3390/polym15071650. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piezoelectric Behaviour in Biodegradable Carrageenan and Iron (III) Oxide Based Sensor.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 17;24(14):4622. doi: 10.3390/s24144622. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39066021 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma proteome responses in zebrafish following λ-carrageenan-Induced inflammation are mediated by PMN leukocytes and correlate highly with their human counterparts.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 29;13:1019201. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1019201. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36248846 Free PMC article.
-
Carrageenan in the Diet: Friend or Foe for Inflammatory Bowel Disease?Nutrients. 2024 Jun 6;16(11):1780. doi: 10.3390/nu16111780. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892712 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Necas J., Bartosikova L. Carrageenan: A review. Vet. Med. 2013;58:187–205. doi: 10.17221/6758-VETMED. - DOI
-
- Besednova N.N., Zvyagintseva T.N., Kuznetsova T.A., Makarenkova I.D., Smolina T.P., Fedyanina L.N., Kryzhanovsky S.P., Zaporozhets T.S. Marine Algae Metabolites as Promising Therapeutics for the Prevention and Treatment of HIV/AIDS. Metabolites. 2019;9:87. doi: 10.3390/metabo9050087. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kalsoom Khan A., Saba A.U., Nawazish S., Akhtar F., Rashid R., Mir S., Nasir B., Iqbal F., Afzal S., Pervaiz F., et al. Carrageenan Based Bionanocomposites as Drug Delivery Tool with Special Emphasis on the Influence of Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017;2017:8158315. doi: 10.1155/2017/8158315. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

