Partial Replacement of Dietary Fat with Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatic Inflammation in Sprague-Dawley Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet
- PMID: 34682732
- PMCID: PMC8535618
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph182010986
Partial Replacement of Dietary Fat with Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatic Inflammation in Sprague-Dawley Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet
Abstract
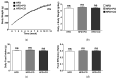
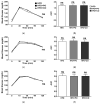
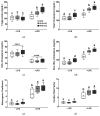
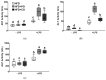
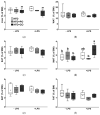
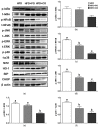
In this study, we investigated whether the partial replacement of dietary fat with polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) ameliorated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced hepatic inflammation in rats fed a high-fat diet. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into three groups and provided each of the following diets: (1) high-fat diet (HFD), (2) HFD with perilla oil (PO), and (3) HFD with corn oil (CO). After 12 weeks of dietary intervention, the rats were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (5 mg/kg) from Escherichia coli O55:B5 or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Following LPS stimulation, serum insulin levels were increased, while PO and CO lowered the serum levels of glucose and insulin. In the liver, LPS increased the triglyceride levels, while PO and CO alleviated the LPS-induced hepatic triglyceride accumulation. In the LPS injected rats, the mRNA expression of genes related to inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress was attenuated by PO and CO in the liver. Furthermore, hepatic levels of proteins involved in the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways, antioxidant response, and ER stress were lowered by PO- and CO-replacement. Therefore, the partial replacement of dietary fat with PUFAs alleviates LPS-induced hepatic inflammation during HFD consumption, which may decrease metabolic abnormalities.
Keywords: corn oil; high-fat diet; inflammation; lipopolysaccharide; perilla oil; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Tay J., Thompson C.H., Luscombe-Marsh N., Wycherley T., Noakes M., Buckley J., Wittert G., Yancy W.S., Jr., Brinkworth G.D. Effects of an energy-restricted low-carbohydrate, high unsaturated fat/low saturated fat diet versus a high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet in type 2 diabetes: A 2-year randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017;20:858–871. doi: 10.1111/dom.13164. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

