Sinus Lift and Implant Insertion on 3D-Printed Polymeric Maxillary Models: Ex Vivo Training for In Vivo Surgical Procedures
- PMID: 34682841
- PMCID: PMC8538196
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10204718
Sinus Lift and Implant Insertion on 3D-Printed Polymeric Maxillary Models: Ex Vivo Training for In Vivo Surgical Procedures
Abstract
Background and objectives: The aim of this study is to demonstrate the increased efficiency achieved by dental practitioners when carrying out an ex vivo training process on 3D-printed maxillaries before performing in vivo surgery.
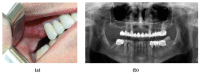
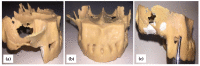
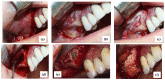
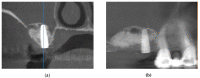
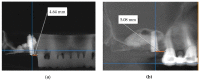
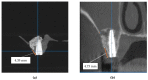
Materials and methods: This developed ex vivo procedure comprises the following phases: (i) scanning the area of interest for surgery; (ii) obtaining a 3D virtual model of this area using Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT); (iii) obtaining a 3D-printed model (based on the virtual one), on which (iv) the dental practitioner simulates/rehearses ex vivo (most of) the surgery protocol; (v) assess with a new CBCT the 3D model after simulation. The technical steps of sinus augmentation and implant insertion could be performed on the corresponding 3D-printed hemi-maxillaries prior to the real in vivo surgery. Two study groups were considered, with forty patients divided as follows: Group 1 comprises twenty patients on which the developed simulation and rehearsal procedure was applied; Group 2 is a control one which comprises twenty patients on which similar surgery was performed without this procedure (considered in order to compare operative times without and with rehearsals).
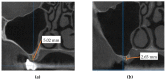
Results: Following the ex vivo training/rehearsal, an optimal surgery protocol was developed for each considered case. The results of the surgery on patients were compared with the results obtained after rehearsals on 3D-printed models. The performed quantitative assessment proved that, using the proposed training procedure, the results of the in vivo surgery are not significantly different (p = 0.089) with regard to the ex vivo simulation for both the mezio-distal position of the implant and the distance from the ridge margin to sinus window. On the contrary, the operative time of Group 1 was reduced significantly (p = 0.001), with an average of 20% with regard to in vivo procedures performed without rehearsals (on the control Group 2).
Conclusions: The study demonstrated that the use of 3D-printed models can be beneficial to dental surgeon practitioners, as well as to students who must be trained before performing clinical treatments.
Keywords: 3D printing; CAD/CAM techniques; Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT); dental implants; ex vivo training procedure; in vivo surgery procedure; maxillary models; polymers; sinus lift.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Cristache C.M., Totu E.E., Iorgulescu G., Pantazi A., Dorobantu D., Nechifor A.C., Isildak I., Burlibasa M., Nechifor G., Enachescu M. Eighteen Months Follow-Up with Patient-Centered Outcomes Assessment of Complete Dentures Manufactured Using a Hybrid Nanocomposite and Additive CAD/CAM Protocol. J. Clin. Med. 2020;9:324. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020324. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Attia S., Narberhaus C., Schaaf H., Streckbein P., Pons-Kühnemann J., Schmitt C., Neukam F.W., Howaldt H.-P., Böttger S. Long-Term Influence of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) on Dental Implants after Maxillary Augmentation: Implant Survival and Success Rates. J. Clin. Med. 2020;9:391. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020391. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

