Systematic Review: Microfluidics and Plasmodium
- PMID: 34683295
- PMCID: PMC8538353
- DOI: 10.3390/mi12101245
Systematic Review: Microfluidics and Plasmodium
Abstract
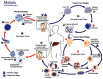
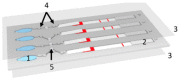
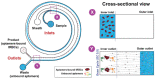
Malaria affects 228 million people worldwide each year, causing severe disease and worsening the conditions of already vulnerable populations. In this review, we explore how malaria has been detected in the past and how it can be detected in the future. Our primary focus is on finding new directions for low-cost diagnostic methods that unspecialized personnel can apply in situ. Through this review, we show that microfluidic devices can help pre-concentrate samples of blood infected with malaria to facilitate the diagnosis. Importantly, these devices can be made cheaply and be readily deployed in remote locations.
Keywords: Peru; lab on a chip; microfluidics; plasmodium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Droplet microfluidics platform for highly sensitive and quantitative detection of malaria-causing Plasmodium parasites based on enzyme activity measurement.ACS Nano. 2012 Dec 21;6(12):10676-83. doi: 10.1021/nn3038594. Epub 2012 Nov 7. ACS Nano. 2012. PMID: 23121492 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical POC device for fast malaria quantitative diagnosis in whole blood by using magnetic beads, Poly-HRP and microfluidic paper electrodes.Biosens Bioelectron. 2020 Feb 15;150:111925. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.111925. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020. PMID: 31818756
-
A lab-on-chip for malaria diagnosis and surveillance.Malar J. 2014 May 9;13:179. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-179. Malar J. 2014. PMID: 24885206 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic nanoparticles in microfluidics-based diagnostics: an appraisal.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2021 Jun;16(15):1329-1342. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2021-0007. Epub 2021 May 24. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34027677 Review.
-
Microfluidic approaches to malaria pathogenesis.Cell Microbiol. 2008 Oct;10(10):1968-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01216.x. Epub 2008 Aug 27. Cell Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18754851 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidic Distillation System for Separation of Propionic Acid in Foods.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 May 28;14(6):1133. doi: 10.3390/mi14061133. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37374718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Team, Global Malaria Programme World Malaria Report 2019. [(accessed on 3 October 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565721.
-
- Cabezas C. Pruebas rápidas para el diagnóstico de la malaria: Una necesidad en áreas rurales con limitado acceso al diagnóstico microscópico. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Pública. 2006;23:79–80.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

