Towards Advances in Medicinal Plant Antimicrobial Activity: A Review Study on Challenges and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 34683362
- PMCID: PMC8541629
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9102041
Towards Advances in Medicinal Plant Antimicrobial Activity: A Review Study on Challenges and Future Perspectives
Abstract
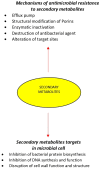
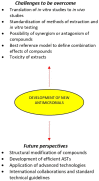
The increasing incidence of drug- resistant pathogens raises an urgent need to identify and isolate new bioactive compounds from medicinal plants using standardized modern analytical procedures. Medicinal plant-derived compounds could provide novel straightforward approaches against pathogenic bacteria. This review explores the antimicrobial activity of plant-derived components, their possible mechanisms of action, as well as their chemical potential. The focus is put on the current challenges and future perspectives surrounding medicinal plants antimicrobial activity. There are some inherent challenges regarding medicinal plant extracts and their antimicrobial efficacy. Appropriate and optimized extraction methodology plant species dependent leads to upgraded and selective extracted compounds. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests for the determination of the antimicrobial activity of plant extracts may show variations in obtained results. Moreover, there are several difficulties and problems that need to be overcome for the development of new antimicrobials from plant extracts, while efforts have been made to enhance the antimicrobial activity of chemical compounds. Research on the mechanisms of action, interplay with other substances, and the pharmacokinetic and/or pharmacodynamic profile of the medicinal plant extracts should be given high priority to characterize them as potential antimicrobial agents.
Keywords: antimicrobial activity; bioactive compounds; challenges; future perspectives; medicinal plants; new antimicrobials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Christenhusz M., Byng J. The Number of Known Plants Species in the World Aand its Annual Increase. Phytotaxa. 2016;261:21–217. doi: 10.11646/phytotaxa.261.3.1. - DOI
-
- MNPS Medicinal Plant Names Services (MNPS) [(accessed on 14 August 2021)]. Available online: https://www.kew.org/science/our-science/science-services/medicinal-plant....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources