L-Carnitine Tartrate Supplementation for 5 Weeks Improves Exercise Recovery in Men and Women: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- PMID: 34684429
- PMCID: PMC8541253
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13103432
L-Carnitine Tartrate Supplementation for 5 Weeks Improves Exercise Recovery in Men and Women: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
L-carnitine tartrate has been shown to improve relatively short-term recovery among athletes. However, there is a lack of research on the longer-term effects in the general population.
Objective: The primary objectives of this randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial were to evaluate the effects of daily L-carnitine tartrate supplementation for 5 weeks on recovery and fatigue.
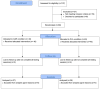
Method: In this study, eighty participants, 21- to 65-years-old, were recruited. Participants were split into two groups of forty participants each, a placebo, and a L-carnitine Tartrate group. Seventy-three participants completed a maintenance exercise training program that culminated in a high-volume exercise challenge.
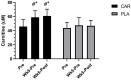
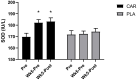
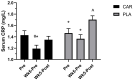
Results: Compared to placebo, L-carnitine tartrate supplementation was able to improve perceived recovery and soreness (p = 0.021), and lower serum creatine kinase (p = 0.016). In addition, L-carnitine tartrate supplementation was able to blunt declines in strength and power compared to placebo following an exercise challenge. Two sub-analyses indicated that these results were independent of gender and age. Interestingly, serum superoxide dismutase levels increased significantly among those supplementing with L-carnitine tartrate.
Conclusions: These findings agree with previous observations among healthy adult subjects and demonstrate that L-carnitine tartrate supplementation beyond 35 days is beneficial for improving recovery and reducing fatigue following exercise across gender and age.
Keywords: L-carnitine tartrate; carnitine; exercise; fatigue; muscle damage antioxidant; muscle power; muscle strength; recovery.
Conflict of interest statement
S.D. and A.B. are employees of Lonza Consumer Health Inc. Other authors have no other relevant affiliations or competing financial involvement with the subject matter or materials in this manuscript. All projects reported in this manuscript were funded by Lonza Consumer Health Inc. (Morrison, NJ, USA).
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

