Actions of Camptothecin Derivatives on Larvae and Adults of the Arboviral Vector Aedes aegypti
- PMID: 34684807
- PMCID: PMC8540655
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26206226
Actions of Camptothecin Derivatives on Larvae and Adults of the Arboviral Vector Aedes aegypti
Abstract
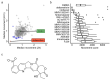
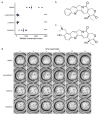
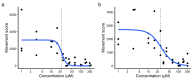
Mosquito-borne viruses including dengue, Zika, and Chikungunya viruses, and parasites such as malaria and Onchocerca volvulus endanger health and economic security around the globe, and emerging mosquito-borne pathogens have pandemic potential. However, the rapid spread of insecticide resistance threatens our ability to control mosquito vectors. Larvae of Aedes aegypti were screened with the Medicines for Malaria Venture Pandemic Response Box, an open-source compound library, using INVAPP, an invertebrate automated phenotyping platform suited to high-throughput chemical screening of larval motility. We identified rubitecan (a synthetic derivative of camptothecin) as a hit compound that reduced A. aegypti larval motility. Both rubitecan and camptothecin displayed concentration dependent reduction in larval motility with estimated EC50 of 25.5 ± 5.0 µM and 22.3 ± 5.4 µM, respectively. We extended our investigation to adult mosquitoes and found that camptothecin increased lethality when delivered in a blood meal to A. aegypti adults at 100 µM and 10 µM, and completely blocked egg laying when fed at 100 µM. Camptothecin and its derivatives are inhibitors of topoisomerase I, have known activity against several agricultural pests, and are also approved for the treatment of several cancers. Crucially, they can inhibit Zika virus replication in human cells, so there is potential for dual targeting of both the vector and an important arbovirus that it carries.
Keywords: Aedes; camptothecin; insecticide; mosquito; rubitecan; vector.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of deltamethrin-resistance in Aedes albopictus on its fitness cost and vector competence.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Apr 27;15(4):e0009391. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009391. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 33905415 Free PMC article.
-
Surveillance of Aedes aegypti populations in the city of Praia, Cape Verde: Zika virus infection, insecticide resistance and genetic diversity.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Sep 21;13(1):481. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04356-z. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32958043 Free PMC article.
-
Management of insecticide resistance in the major Aedes vectors of arboviruses: Advances and challenges.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Oct 10;13(10):e0007615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007615. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31600206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distribution of insecticide resistance and mechanisms involved in the arbovirus vector Aedes aegypti in Laos and implication for vector control.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Dec 12;13(12):e0007852. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007852. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31830027 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral Compounds for Blocking Arboviral Transmission in Mosquitoes.Viruses. 2021 Jan 14;13(1):108. doi: 10.3390/v13010108. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33466915 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biotechnology for micropropagation and camptothecin production in Ophiorrhiza sp.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;106(11):3851-3877. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11941-y. Epub 2022 May 21. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35596786 Review.
References
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–1788. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

