Lipid A-Mediated Bacterial-Host Chemical Ecology: Synthetic Research of Bacterial Lipid As and Their Development as Adjuvants
- PMID: 34684874
- PMCID: PMC8538916
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26206294
Lipid A-Mediated Bacterial-Host Chemical Ecology: Synthetic Research of Bacterial Lipid As and Their Development as Adjuvants
Abstract
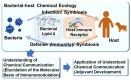
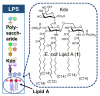
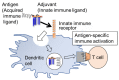
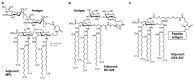
Gram-negative bacterial cell surface component lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and its active principle, lipid A, exhibit immunostimulatory effects and have the potential to act as adjuvants. However, canonical LPS acts as an endotoxin by hyperstimulating the immune response. Therefore, LPS and lipid A must be structurally modified to minimize their toxic effects while maintaining their adjuvant effect for application as vaccine adjuvants. In the field of chemical ecology research, various biological phenomena occurring among organisms are considered molecular interactions. Recently, the hypothesis has been proposed that LPS and lipid A mediate bacterial-host chemical ecology to regulate various host biological phenomena, mainly immunity. Parasitic and symbiotic bacteria inhabiting the host are predicted to possess low-toxicity immunomodulators due to the chemical structural changes of their LPS caused by co-evolution with the host. Studies on the chemical synthesis and functional evaluation of their lipid As have been developed to test this hypothesis and to apply them to low-toxicity and safe adjuvants.
Keywords: Alcaligenes faecalis; adjuvant; chemical biology; chemical ecology; glycolipid; lipid A; lipopolysaccharide; natural product chemistry; symbiotic bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Kusumoto S., Fukase K., Shiba T. Key structures of bacterial peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide triggering the innate immune system of higher animals: Chemical synthesis and functional studies. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2010;86:322–337. doi: 10.2183/pjab.86.322. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coley W.B. The treatment of malignant tumors by repeated inoculations of erysipelas. With a report of ten original cases. 1893. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1991;262:3–11. - PubMed
-
- Fujimoto Y., Shimoyama A., Saeki A., Kitayama N., Kasamatsu C., Tsutsui H., Fukase K. Innate immunomodulation by lipophilic termini of lipopolysaccharide; synthesis of lipid As from Porphyromonas gingivalis and other bacteria and their immunomodulative responses. Mol. Biosyst. 2013;9:9876–9896. doi: 10.1039/c3mb25477a. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

