Biosensing Using SERS Active Gold Nanostructures
- PMID: 34685120
- PMCID: PMC8539114
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11102679
Biosensing Using SERS Active Gold Nanostructures
Abstract
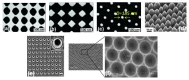
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) has become a powerful tool for biosensing applications owing to its fingerprint recognition, high sensitivity, multiplex detection, and biocompatibility. This review provides an overview of the most significant aspects of SERS for biomedical and biosensing applications. We first introduced the mechanisms at the basis of the SERS amplifications: electromagnetic and chemical enhancement. We then illustrated several types of substrates and fabrication methods, with a focus on gold-based nanostructures. We further analyzed the relevant factors for the characterization of the SERS sensor performances, including sensitivity, reproducibility, stability, sensor configuration (direct or indirect), and nanotoxicity. Finally, a representative selection of applications in the biomedical field is provided.
Keywords: SERS; biosensing; gold nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Zheng Y.B., Jensen L., Yan W., Walker T.R., Juluri B.K., Jensen L., Huang T.J. Chemically tuning the localized surface plasmon resonances of gold nanostructure arrays. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2009;113:7019–7024. doi: 10.1021/jp8106606. - DOI
-
- Kahraman M., Mullen E.R., Korkmaz A., Wachsmann-Hogiu S. Fundamentals and applications of SERS-based bioanalytical sensing. Nanophotonics. 2017;6:831–852. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2016-0174. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

