Ionic and Enzymatic Multiple-Crosslinked Nanogels for Drug Delivery
- PMID: 34685323
- PMCID: PMC8541401
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13203565
Ionic and Enzymatic Multiple-Crosslinked Nanogels for Drug Delivery
Abstract
Both ionic and enzymatic crosslink are efficient strategies for constructing network materials of high biocompatibility. Here chitosan was modified firstly and then crosslinked by these two methods for complementary advantages. The preparation methods and ionic crosslinkers can regulate the size and uniformity of the multiple-crosslinked nanogels. The multiple-crosslinked nanogels with the smallest size and the best uniformity was selected for the drug delivery. The drug-loading content and encapsulation efficiency were up to 35.01 and 66.82%, respectively. Their release behaviours are correlated with the pH value and the drug dosage. In general, the lower pH value and the lower drug dosage promoted the drug release. With the assistance of several kinetic models, it is found that drug diffusion plays a preponderant role in drug release, while polymer relaxation has a subtle effect. The multiple-crosslink resulting from ionic compounds and enzymes may provide a new perspective on developing novel biocompatible materials.
Keywords: drug delivery; enzymatic crosslink; ionic crosslink; multiple-crosslinked nanogel; natural polymeric materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

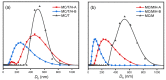



References
-
- Wang W., Liu X., Xie Y., Zhang H., Yu W., Xiong Y., Xie W., Ma X. Microencapsulation using natural polysaccharides for drug delivery and cell implantation. J. Mater. Chem. 2006;16:3252. doi: 10.1039/b603595g. - DOI
-
- Nigmatullin R., Thomas P., Lukasiewicz B., Puthussery H., Roy I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates, a family of natural polymers, and their applications in drug delivery. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015;90:1209–1221. doi: 10.1002/jctb.4685. - DOI
-
- Tong X., Pan W., Su T., Zhang M., Dong W., Qi X. Recent advances in natural polymer-based drug delivery systems. React. Funct. Polym. 2020;148:104501. doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2020.104501. - DOI
-
- Luo K., Yang Y., Shao Z. Physically crosslinked biocompatible silk-fibroin-based hydrogels with high mechanical performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016;26:872–880. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201503450. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

