Quantifying Renin-Angiotensin-System Alterations in COVID-19
- PMID: 34685735
- PMCID: PMC8535134
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10102755
Quantifying Renin-Angiotensin-System Alterations in COVID-19
Abstract
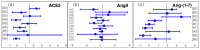
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plays a pivotal role in a wide series of physiological processes, among which inflammation and blood pressure regulation. One of its key components, the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, has been identified as the entry point of the SARS-CoV-2 virus into the host cells, and therefore a lot of research has been devoted to study RAS dysregulation in COVID-19. Here we discuss the alterations of the regulatory RAS axes due to SARS-CoV-2 infection on the basis of a series of recent clinical investigations and experimental analyzes quantifying, e.g., the levels and activity of RAS components. We performed a comprehensive meta-analysis of these data in view of disentangling the links between the impaired RAS functioning and the pathophysiological characteristics of COVID-19. We also review the effects of several RAS-targeting drugs and how they could potentially help restore the normal RAS functionality and minimize the COVID-19 severity. Finally, we discuss the conflicting evidence found in the literature and the open questions on RAS dysregulation in SARS-CoV-2 infection whose resolution would improve our understanding of COVID-19.
Keywords: ACE2; Angiotensin II; Angiotensin-(1-7); RAS dysregulation; RAS-targeting drugs; SARS-CoV-2; spike protein.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Raizada M.K., Phillips M.I., Sumners C. Cellular and Molecular Biology of the Renin-Angiotensin System. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 1993.
-
- Casarini D.E., Arita D.Y., Cunha T.S., Colucci J.A. New Aspects of the Renin Angiotensin System in Cardiovascular and Renal Diseases. Bentham; Sharjah, United Arab Emirates: 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

