Phospholipids in Salt Stress Response
- PMID: 34686013
- PMCID: PMC8540237
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10102204
Phospholipids in Salt Stress Response
Abstract
High salinity threatens crop production by harming plants and interfering with their development. Plant cells respond to salt stress in various ways, all of which involve multiple components such as proteins, peptides, lipids, sugars, and phytohormones. Phospholipids, important components of bio-membranes, are small amphoteric molecular compounds. These have attracted significant attention in recent years due to the regulatory effect they have on cellular activity. Over the past few decades, genetic and biochemical analyses have partly revealed that phospholipids regulate salt stress response by participating in salt stress signal transduction. In this review, we summarize the generation and metabolism of phospholipid phosphatidic acid (PA), phosphoinositides (PIs), phosphatidylserine (PS), phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and phosphatidylglycerol (PG), as well as the regulatory role each phospholipid plays in the salt stress response. We also discuss the possible regulatory role based on how they act during other cellular activities.
Keywords: phosphatidic acid; phosphatidylcholine; phosphatidylethanolamine; phosphatidylglycerol; phosphatidylserine; phosphoinositide; phospholipids; salt stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
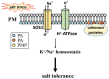
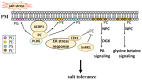
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

