Inhibition of hypoxia-induced Mucin 1 alters the proteomic composition of human osteoblast-produced extracellular matrix, leading to reduced osteogenic and angiogenic potential
- PMID: 34687046
- PMCID: PMC9298310
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.30617
Inhibition of hypoxia-induced Mucin 1 alters the proteomic composition of human osteoblast-produced extracellular matrix, leading to reduced osteogenic and angiogenic potential
Abstract
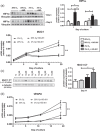
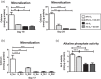
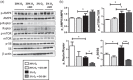
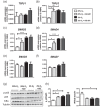
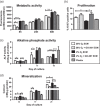
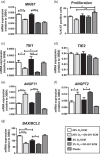
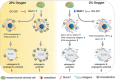
The bone microenvironment is one of the most hypoxic regions of the human body and in experimental models; hypoxia inhibits osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs). Our previous work revealed that Mucin 1 (MUC1) was dynamically expressed during osteogenic differentiation of human MSCs and upregulated by hypoxia. Upon stimulation, its C-terminus (MUC1-CT) is proteolytically cleaved, translocases to the nucleus, and binds to promoters of target genes. Therefore, we assessed the MUC1-mediated effect of hypoxia on the proteomic composition of human osteoblast-derived extracellular matrices (ECMs) and characterized their osteogenic and angiogenic potentials in the produced ECMs. We generated ECMs from osteogenically differentiated human MSC cultured in vitro under 20% or 2% oxygen with or without GO-201, a MUC1-CT inhibitor. Hypoxia upregulated MUC1, vascular endothelial growth factor, and connective tissue growth factor independent of MUC1 inhibition, whereas GO-201 stabilized hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha. Hypoxia and/or MUC1-CT inhibition reduced osteogenic differentiation of human MSC by AMP-activated protein kinase/mTORC1/S6K pathway and dampened their matrix mineralization. Hypoxia modulated ECMs by transforming growth factor-beta/Smad and phosphorylation of NFκB and upregulated COL1A1, COL5A1, and COL5A3. The ECMs of hypoxic osteoblasts reduced MSC proliferation and accelerated their osteogenic differentiation, whereas MUC1-CT-inhibited ECMs counteracted these effects. In addition, ECMs generated under MUC1-CT inhibition reduced the angiogenic potential independent of oxygen concentration. We claim here that MUC1 is critical for hypoxia-mediated changes during osteoblastogenesis, which not only alters the proteomic landscape of the ECM but thereby also modulates its osteogenic and angiogenic potentials.
Keywords: angiogenesis; extracellular matrix; human osteoblasts; hypoxia; mucin-1.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Physiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative proteomic profiling of human osteoblast-derived extracellular matrices identifies proteins involved in mesenchymal stromal cell osteogenic differentiation and mineralization.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan;233(1):387-395. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25898. Epub 2017 May 19. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28272740
-
Differential growth factor adsorption to calvarial osteoblast-secreted extracellular matrices instructs osteoblastic behavior.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025990. Epub 2011 Oct 5. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21998741 Free PMC article.
-
Cultured cell-derived extracellular matrices to enhance the osteogenic differentiation and angiogenic properties of human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019 Sep;13(9):1544-1558. doi: 10.1002/term.2907. Epub 2019 Jul 10. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019. PMID: 31151132
-
Osteoblast recruitment to sites of bone formation in skeletal development, homeostasis, and regeneration.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2013 Sep;99(3):170-91. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.21047. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2013. PMID: 24078495 Review.
-
Oxygen sensing and osteogenesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Nov;1117:1-11. doi: 10.1196/annals.1402.049. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18056033 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-210-3p protects against osteoarthritis through inhibiting subchondral angiogenesis by targeting the expression of TGFBR1 and ID4.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 29;13:982278. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.982278. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36263050 Free PMC article.
-
A transcriptomic analysis of dental pulp stem cell senescence in vitro.Biomed Eng Online. 2024 Oct 18;23(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12938-024-01298-w. Biomed Eng Online. 2024. PMID: 39425139 Free PMC article.
-
Tibial plateau fracture and RNA sequencing with osteogenesis imperfecta: a case report.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 9;14:1164386. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1164386. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37229455 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic signatures of severe acute mountain sickness during rapid ascent to 4,300 m.Front Physiol. 2025 Jan 29;15:1477070. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1477070. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39944919 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Immune Cells during Bone Injury Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 23;24(19):14484. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914484. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37833933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aubert, S. , Fauquette, V. , Hémon, B. , Lepoivre, R. , Briez, N. , Bernard, D. , Van Seuningen, I. , Leroy, X. , & Perrais, M. (2009). MUC1, a new hypoxia inducible factor target gene, is an actor in clear renal cell carcinoma tumor progression. Cancer Research, 69(14), 5707–5715. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4905 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baroncelli, M. , van der Eerden, B. C. , Kan, Y.‐Y. , Alves, R. D. , Demmers, J. A. , van de Peppel, J. , & van Leeuwen, J. P. (2018). Comparative proteomic profiling of human osteoblast‐derived extracellular matrices identifies proteins involved in mesenchymal stromal cell osteogenic differentiation and mineralization. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 233(1), 387–395. 10.1002/jcp.25898 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beauchef, G. , Bigot, N. , Kypriotou, M. , Renard, E. , Porée, B. , Widom, R. , Dompmartin‐Blanchere, A. , Oddos, T. , Maquart, F. X. , Demoor, M. , Boumediene, K. , Galera, P. 2012. The p65 subunit of NF‐κB inhibits COL1A1 gene transcription in human dermal and scleroderma fibroblasts through its recruitment on promoter by protein interaction with transcriptional activators (c‐Krox, Sp1, and Sp3). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287(5), 3462–3478. 10.1074/jbc.M111.286443 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

