ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in perspective of deceased donor transplantation and induction strategies: a propensity-matched analysis
- PMID: 34687095
- PMCID: PMC9299000
- DOI: 10.1111/tri.14145
ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in perspective of deceased donor transplantation and induction strategies: a propensity-matched analysis
Abstract
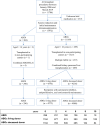
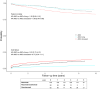
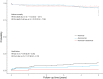
Kidney transplant candidates are blood group incompatible with roughly one out of three potential living donors. We compared outcomes after ABO-incompatible (ABOi) kidney transplantation with matched ABO-compatible (ABOc) living and deceased donor transplantation and analyzed different induction regimens. We performed a retrospective study with propensity matching and compared patient and death-censored graft survival after ABOi versus ABOc living donor and deceased donor kidney transplantation in a nationwide registry from 2006 till 2019. 296 ABOi were compared with 1184 center and propensity-matched ABOc living donor and 1184 deceased donor recipients (matching: recipient age, sex, blood group, and PRA). Patient survival was better compared with deceased donor [hazard ratio (HR) for death of HR 0.69 (0.49-0.96)] and non-significantly different from ABOc living donor recipients [HR 1.28 (0.90-1.81)]. Rate of graft failure was higher compared with ABOc living donor transplantation [HR 2.63 (1.72-4.01)]. Rejection occurred in 47% of 140 rituximab versus 22% of 50 rituximab/basiliximab, and 4% of 92 alemtuzumab-treated recipients (P < 0.001). ABOi kidney transplantation is superior to deceased donor transplantation. Rejection rate and graft failure are higher compared with matched ABOc living donor transplantation, underscoring the need for further studies into risk stratification and induction therapy [NTR7587, www.trialregister.nl].
Keywords: ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation; alemtuzumab; deceased donor transplantation; living donor transplantation; patient and graft survival; rejection.
© 2021 The Authors. Transplant International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Steunstichting ESOT.
Conflict of interest statement
Jan AJG van den Brand is part‐time employed by and has stock options for Binnovate Digital Health B.V. Binnovate Digital Health was not involved in the present research. The other authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by
Figures
Comment in
-
ABO-Incompatibility: Time to Challenge the Paradigm of Equivalence in Live-Donor Kidney Transplantation?Transpl Int. 2022 Feb 8;35:10281. doi: 10.3389/ti.2022.10281. eCollection 2022. Transpl Int. 2022. PMID: 35210935 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Roodnat JI, van de Wetering J, Claas FH, Ijzermans J, Weimar W. Persistently low transplantation rate of ABO blood type O and highly sensitised patients despite alternative transplantation programs. Transpl Int 2012; 25: 987. - PubMed
-
- Tyden G, Kumlien G, Fehrman I. Successful ABO‐incompatible kidney transplantations without splenectomy using antigen‐specific immunoadsorption and rituximab. Transplantation 2003; 76: 730. - PubMed
-
- Tanabe K, Ishida H, Shimizu T, Omoto K, Shirakawa H, Tokumoto T. Evaluation of two different preconditioning regimens for ABO‐incompatible living kidney donor transplantation. A comparison of splenectomy vs. rituximab‐treated non‐splenectomy preconditioning regimens. Contrib Nephrol 2009; 162: 61. - PubMed
-
- Bentall A, Herrera LP, Cornell LD, et al. Differences in chronic intragraft inflammation between positive crossmatch and ABO‐incompatible kidney transplantation. Transplantation 2014; 98: 1089. - PubMed
-
- Barnett ANR, Manook M, Nagendran M, et al. Tailored desensitization strategies in ABO blood group antibody incompatible renal transplantation. Transpl Int 2014; 27: 187. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

