Bimekizumab for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: efficacy, safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and transcriptomics from a phase IIa, randomized, double-blind multicentre study
- PMID: 34687214
- PMCID: PMC9303624
- DOI: 10.1111/bjd.20827
Bimekizumab for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: efficacy, safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and transcriptomics from a phase IIa, randomized, double-blind multicentre study
Abstract
Background: Bimekizumab is a monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits both interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-17F, which is currently under investigation for treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Maintenance dosing every 4 weeks is well established with IL-17 inhibitors for psoriasis.
Objectives: To investigate the possible dosing interval during bimekizumab maintenance therapy to maintain clear skin, to inform phase III studies.
Methods: Forty-nine patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis received bimekizumab 320 mg at weeks 0/4, followed at week 16 by bimekizumab 320 mg (n = 17) or placebo (n = 32). Efficacy, safety, pharmacokinetics, immunogenicity and biopsy transcriptomic analyses were assessed to week 28.
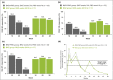
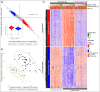
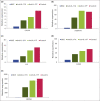
Results: At week 8, 47% of patients achieved a 100% improvement from baseline in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 100), increasing to 57% at week 12 (8 weeks after the second dose) before decreasing. In those who received bimekizumab at week 16, PASI 100 rate increased to comparable peak levels at week 20, but reduced by week 28 to 41% (12 weeks after the third dose). The week 8 transcriptional signature observed in lesional psoriatic skin rapidly normalized to levels consistent with nonlesional skin, resulting in molecular remission. Keratinocyte-related gene products such as CXCL1 (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1), IL-8 (encoded by the CXCL8 gene), CCL20 (C-C motif chemokine 20), IL-36γ and IL-17C were profoundly normalized to levels associated with nonlesional skin.
Conclusions: Here, inhibition of IL-17F in addition to IL-17A resulted in rapid, deep clinical responses. Additionally, profound normalization of keratinocyte biology and the psoriatic transcriptome was observed, including normalization of both IL17 and IL23 gene expression by week 8. These data provide evidence to support evaluation of bimekizumab maintenance dosing both every 8 and every 4 weeks in phase III clinical trials.
© 2021 The Authors. British Journal of Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Association of Dermatologists.
Figures





Comment in
-
Another anti-interleukin (IL)-17 inhibitor: is there an advantage of blocking IL-17A and IL-17F?Br J Dermatol. 2022 Apr;186(4):603-604. doi: 10.1111/bjd.20959. Br J Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35377958 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gordon KB, Strober B, Lebwohl M et al. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab in moderate‐to‐severe plaque psoriasis (UltIMMa‐1 and UltIMMa‐2): results from two double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled and ustekinumab‐controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet 2018; 392:650–61. - PubMed
-
- Reich K, Armstrong AW, Langley RG et al. Guselkumab versus secukinumab for the treatment of moderate‐to‐severe psoriasis (ECLIPSE): results from a phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019; 394:831–9. - PubMed
-
- Blauvelt A, Reich K, Tsai T‐F et al. Secukinumab is superior to ustekinumab in clearing skin of subjects with moderate‐to‐severe plaque psoriasis up to 1 year: results from the CLEAR study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2017; 76:60–9.e9. - PubMed
-
- Langley R, Papp K, Gooderham M et al. Efficacy and safety of continuous every‐2‐week dosing of ixekizumab over 52 weeks in patients with moderate‐to‐severe plaque psoriasis in a randomized phase III trial (IXORA‐P). Br J Dermatol 2018; 178:1315–23. - PubMed

