Liver fibrosis assessment: MR and US elastography
- PMID: 34687329
- PMCID: PMC9033887
- DOI: 10.1007/s00261-021-03269-4
Liver fibrosis assessment: MR and US elastography
Abstract
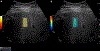
Elastography has emerged as a preferred non-invasive imaging technique for the clinical assessment of liver fibrosis. Elastography methods provide liver stiffness measurement (LSM) as a surrogate quantitative biomarker for fibrosis burden in chronic liver disease (CLD). Elastography can be performed either with ultrasound or MRI. Currently available ultrasound-based methods include strain elastography, two-dimensional shear wave elastography (2D-SWE), point shear wave elastography (pSWE), and vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE). MR Elastography (MRE) is widely available as two-dimensional gradient echo MRE (2D-GRE-MRE) technique. US-based methods provide estimated Young's modulus (eYM) and MRE provides magnitude of the complex shear modulus. MRE and ultrasound methods have proven to be accurate methods for detection of advanced liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Other clinical applications of elastography include liver decompensation prediction, and differentiation of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) from simple steatosis (SS). In this review, we briefly describe the different elastography methods, discuss current clinical applications, and provide an overview of advances in the field of liver elastography.
Keywords: Chronic liver disease; Fibrosis staging; Liver stiffness; Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; Shear stiffness.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations
Figures
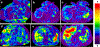
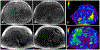
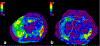
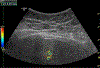

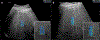
References
-
- Heidelbaugh JJ, Bruderly M (2006) Cirrhosis and chronic liver failure: part I. Diagnosis and evaluation. Am Fam Physician 74 (5):756–762 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

