Avelumab in Combination Regimens for Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL: Results from the Phase Ib JAVELIN DLBCL Study
- PMID: 34687398
- PMCID: PMC8613117
- DOI: 10.1007/s11523-021-00849-8
Avelumab in Combination Regimens for Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL: Results from the Phase Ib JAVELIN DLBCL Study
Abstract
Background: Relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is associated with a poor prognosis despite the availability of multiple treatment options. Preliminary evidence suggests that DLBCL may be responsive to programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1)/programmed death 1 inhibitors.
Objective: The JAVELIN DLBCL study was conducted to assess whether a combination of agents could augment and sustain the antitumor immunity of avelumab, an anti-PD-L1 antibody, in R/R DLBCL.
Methods: This was a multicenter, randomized, open-label, parallel-arm study with a phase Ib and a phase III component. Reported here are the results from the phase Ib study, wherein 29 adult patients with DLBCL were randomized 1:1:1 to receive avelumab in combination with utomilumab (an immunoglobulin G2 4-1BB agonist) and rituximab (arm A), avelumab in combination with utomilumab and azacitidine (arm B), or avelumab in combination with bendamustine and rituximab (arm C). The primary endpoints were dose-limiting toxicities and objective response as assessed by the investigator per Lugano Response Classification criteria.
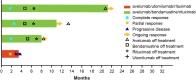
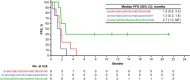
Results: Of the seven patients in arm A, one (14.3%) experienced two grade 3 dose-limiting toxicities (herpes zoster and ophthalmic herpes zoster); no dose-limiting toxicities were reported in arms B or C. No new safety concerns emerged for avelumab. One partial response was reported in arm A, three complete responses in arm C, and no responses in arm B. Given the insufficient antitumor activity in arms A and B and the infeasibility of expanding arm C, the study was discontinued before initiation of the phase III component.
Conclusions: The low level of clinical activity suggests that PD-L1 inhibitor activity may be limited in R/R DLBCL. CLINICALTRIALS.
Gov identifier: NCT02951156.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
EAH has received honoraria for advisory work for Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, MSD, Gilead, Antigene, Janssen, and AstraZeneca; travel expenses and honoraria for speaker work for Roche; and research funding from Roche, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, MSD, Gilead, Antigene, Janssen, and AstraZeneca. TP has acted in consultancy/advisory roles for AbbVie, ADC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Incyte, Genentech, Gilead, Kite, and Pharmacyclics and has received research funding from AbbVie, Bayer, BMS/Celgene, Genentech, and Incyte. AS has acted in consultancy/advisory roles for Bristol Myers Squibb, Servier, Gilead, Pfizer, Eisai, Bayer, MSD, Arqule, and Sanofi and has undertaken speaker bureau work for Takeda, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche, AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Servier, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Arqule, Lilly, Sandoz, Eisai, Novartis, Bayer, and MSD. NSS has acted in consultancy/advisory roles for Kite, AbbVie, Janssen, and Kyowa Kirin and has undertaken speaker bureau work for Janssen and AbbVie. GPG has acted in advisory roles for Roche, Novartis, Gilead, and Janssen; and has received honoraria from Roche, AbbVie, and Novartis and research funding from MSD, BeiGene, and Janssen. JR has acted in consultancy/advisory roles for Takeda, Bristol Myers Squibb, ADC Therapeutics, and Novartis; owns stock in AstraZeneca and ADC Therapeutics; has received honoraria from Takeda, ADC Therapeutics, and Bristol Myers Squibb; has provided speaker/expert testimony for Takeda and ADC Therapeutics; and has received research funding from Takeda. KG has received honoraria from and served as a consultant for Amgen, AbbVie, BMS/Celgene, Janssen, Sanofi-Genzyme, Takeda, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, and BeiGene and has received research funding from Amgen, AbbVie, BMS/Celgene, Janssen, Sanofi-Genzyme, Takeda, and Novartis. AT, BH, ADL, and RS are employees of and report stock ownership in Pfizer. SMA has received research funding (paid to his institution) for clinical trials from Bristol Myers Squibb, Seattle Genetics, Takeda, AI Therapeutics, Affimed, Pfizer, Trillium, Regeneron, and ADC Therapeutics. LEB, FR, GV, FO, CQ, and DS have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Figures

References
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. B-cell Lymphomas. v4.2021. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/b-cell.pdf. Accessed 17 June 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

